mirror of
https://github.com/moveit/moveit_task_constructor.git
synced 2025-11-04 14:49:57 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' into ros2
This commit is contained in:
commit
b3d20cdcec
@ -14,6 +14,7 @@ Checks: 'performance-*,
|
||||
readability-redundant-string-cstr,
|
||||
readability-simplify-boolean-expr,
|
||||
readability-container-size-empty,
|
||||
readability-identifier-naming,
|
||||
'
|
||||
HeaderFilterRegex: '.*/moveit/task_constructor/.*\.h'
|
||||
AnalyzeTemporaryDtors: false
|
||||
@ -26,14 +27,14 @@ CheckOptions:
|
||||
value: '2'
|
||||
# type names
|
||||
- key: readability-identifier-naming.ClassCase
|
||||
value: CamelCase
|
||||
value: aNy_CasE # CamelCase
|
||||
- key: readability-identifier-naming.EnumCase
|
||||
value: CamelCase
|
||||
- key: readability-identifier-naming.UnionCase
|
||||
value: CamelCase
|
||||
# method names
|
||||
- key: readability-identifier-naming.MethodCase
|
||||
value: camelBack
|
||||
value: aNy_CasE # camelBack
|
||||
# variable names
|
||||
- key: readability-identifier-naming.VariableCase
|
||||
value: lower_case
|
||||
|
||||
44
.github/workflows/ci.yaml
vendored
44
.github/workflows/ci.yaml
vendored
@ -8,6 +8,11 @@ on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
contents: read
|
||||
pages: write
|
||||
id-token: write
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
default:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
@ -20,19 +25,15 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- IMAGE: rolling-source
|
||||
NAME: ccov
|
||||
TARGET_CMAKE_ARGS: -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug -DCMAKE_CXX_FLAGS="--coverage"
|
||||
CXXFLAGS: >-
|
||||
-Werror -Wall -Wextra -Wwrite-strings -Wunreachable-code -Wpointer-arith
|
||||
- IMAGE: rolling-source
|
||||
CXX: clang++
|
||||
CLANG_TIDY: pedantic
|
||||
CXXFLAGS: >-
|
||||
-Werror -Wall -Wextra -Wwrite-strings -Wunreachable-code -Wpointer-arith
|
||||
-Wno-deprecated-copy
|
||||
# Add fast_unwind_on_malloc=0 to fix stacktraces being too short or do not make sense
|
||||
# see https://github.com/google/sanitizers/wiki/AddressSanitizer
|
||||
# Disable alloc/dealloc mismatch warnings: https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/pull/1324
|
||||
- IMAGE: rolling-source
|
||||
NAME: asan
|
||||
# Add fast_unwind_on_malloc=0 to fix stacktraces being too short or do not make sense
|
||||
# see https://github.com/google/sanitizers/wiki/AddressSanitizer
|
||||
# Disable alloc/dealloc mismatch warnings: https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/pull/1324
|
||||
DOCKER_RUN_OPTS: >-
|
||||
-e PRELOAD=libasan.so.5
|
||||
-e LSAN_OPTIONS="suppressions=$PWD/.github/workflows/lsan.suppressions,fast_unwind_on_malloc=0"
|
||||
@ -40,12 +41,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
TARGET_CMAKE_ARGS: -DCMAKE_CXX_FLAGS="-fsanitize=address -fno-omit-frame-pointer -O1 -g"
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CLANG_TIDY_ARGS: --fix --fix-errors --format-style=file
|
||||
CLANG_TIDY_ARGS: -quiet -export-fixes ${{ github.workspace }}/.work/clang-tidy-fixes.yaml
|
||||
DOCKER_IMAGE: ghcr.io/ros-planning/moveit2:${{ matrix.env.IMAGE }}
|
||||
UNDERLAY: /root/ws_moveit/install
|
||||
# TODO: Port to ROS2
|
||||
# DOWNSTREAM_WORKSPACE: "github:ubi-agni/mtc_demos#master github:TAMS-Group/mtc_pour#master"
|
||||
UPSTREAM_WORKSPACE: .repos
|
||||
CCACHE_DIR: ${{ github.workspace }}/.ccache
|
||||
BASEDIR: ${{ github.workspace }}/.work
|
||||
CACHE_PREFIX: "${{ matrix.env.IMAGE }}${{ contains(matrix.env.TARGET_CMAKE_ARGS, '--coverage') && '-ccov' || '' }}"
|
||||
@ -58,6 +58,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
submodules: recursive
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Cache ccache
|
||||
uses: rhaschke/cache@main
|
||||
@ -72,15 +74,35 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- id: ici
|
||||
name: Run industrial_ci
|
||||
uses: ros-industrial/industrial_ci@master
|
||||
uses: rhaschke/industrial_ci@clang-tidy
|
||||
env: ${{ matrix.env }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Upload ici's target_ws/install folder
|
||||
uses: rhaschke/upload-ici-workspace@main
|
||||
if: success() && matrix.env.CLANG_TIDY
|
||||
with:
|
||||
subdir: target_ws/install
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Upload test artifacts (on failure)
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
|
||||
if: failure() && (steps.ici.outputs.run_target_test || steps.ici.outputs.target_test_results)
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: test-results-${{ matrix.env.IMAGE }}
|
||||
name: test-results-${{ matrix.env.IMAGE }}${{ matrix.env.NAME && '-' || ''}}${{ matrix.env.NAME }}${{ matrix.env.CLANG_TIDY && '-clang-tidy' || '' }}
|
||||
path: ${{ env.BASEDIR }}/target_ws/**/test_results/**/*.xml
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Upload clang-tidy fixes (on failure)
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
|
||||
if: failure() && steps.ici.outputs.clang_tidy_checks
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: clang-tidy-fixes.yaml
|
||||
path: ${{ env.BASEDIR }}/clang-tidy-fixes.yaml
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show clang-tidy warnings
|
||||
if: always() && matrix.env.CLANG_TIDY
|
||||
uses: asarium/clang-tidy-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fixesFile: ${{ env.BASEDIR }}/clang-tidy-fixes.yaml
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate codecov report
|
||||
uses: rhaschke/lcov-action@main
|
||||
if: contains(matrix.env.TARGET_CMAKE_ARGS, '--coverage') && steps.ici.outputs.target_test_results == '0'
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/format.yaml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/format.yaml
vendored
@ -14,6 +14,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
submodules: recursive
|
||||
- name: Install clang-format-12
|
||||
run: sudo apt-get install clang-format-12
|
||||
- uses: pre-commit/action@v3.0.0
|
||||
|
||||
2
.gitignore
vendored
2
.gitignore
vendored
@ -1 +1,3 @@
|
||||
*.swp
|
||||
*.pyc
|
||||
__pycache__/
|
||||
|
||||
5
.gitmodules
vendored
Normal file
5
.gitmodules
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[submodule "core/python/pybind11"]
|
||||
path = core/python/pybind11
|
||||
url = https://github.com/rhaschke/pybind11
|
||||
branch = smart_holder
|
||||
shallow = true
|
||||
@ -32,6 +32,7 @@ repos:
|
||||
rev: 22.3.0
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: black
|
||||
args: ["--line-length", "100"]
|
||||
|
||||
- repo: local
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
@ -41,4 +42,4 @@ repos:
|
||||
entry: clang-format-12
|
||||
language: system
|
||||
files: \.(c|cc|cxx|cpp|frag|glsl|h|hpp|hxx|ih|ispc|ipp|java|js|m|proto|vert)$
|
||||
args: ['-fallback-style=none', '-i']
|
||||
args: ["-fallback-style=none", "-i"]
|
||||
|
||||
5
.repos
5
.repos
@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
|
||||
repositories:
|
||||
rosparam_shortcuts:
|
||||
type: git
|
||||
url: https://github.com/PickNikRobotics/rosparam_shortcuts
|
||||
version: ros2
|
||||
14
README.md
14
README.md
@ -5,9 +5,14 @@ It draws on the planning capabilities of [MoveIt](https://moveit.ros.org/) to so
|
||||
A common interface, based on MoveIt's PlanningScene is used to pass solution hypotheses between stages.
|
||||
The framework enables the hierarchical organization of basic stages using *containers*, allowing for sequential as well as parallel compositions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Video
|
||||
## Videos
|
||||
|
||||
[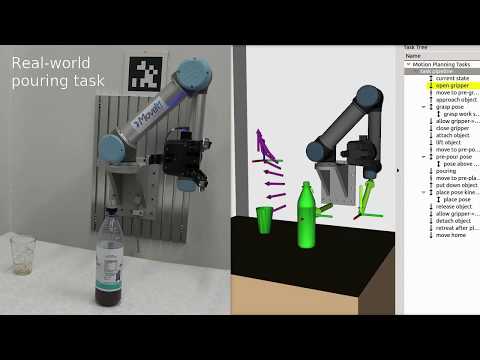](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fCORKVYsdDI)
|
||||
- Demo video associated with [ICRA 2019 paper](https://pub.uni-bielefeld.de/download/2918864/2933599/paper.pdf)
|
||||
|
||||
[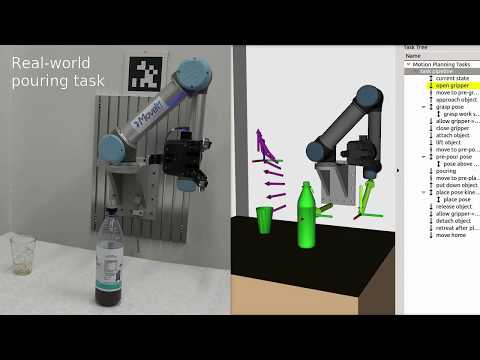](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fCORKVYsdDI)
|
||||
|
||||
- [Presentation @ ROSCon 2018 (Madrid)](https://vimeo.com/293432325)
|
||||
- [Presentation @ MoveIt workshop 2019 (Macau)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a8r7O2bs1Mc)
|
||||
|
||||
## Tutorial
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,10 +37,9 @@ Ideas and requests for other interesting/useful features are welcome.
|
||||
|
||||
If you use this framework in your project, please cite the associated paper:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Michael Görner*, Robert Haschke*, Helge Ritter, and Jianwei Zhang,
|
||||
MoveIt! Task Constructor for Task-Level Motion Planning,
|
||||
International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA 2019, Montreal, Canada.
|
||||
"MoveIt! Task Constructor for Task-Level Motion Planning",
|
||||
_International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)_, 2019, Montreal, Canada.
|
||||
[[DOI]](https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2019.8793898) [[PDF]](https://pub.uni-bielefeld.de/download/2918864/2933599/paper.pdf).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,6 +23,7 @@ add_compile_options(-fvisibility-inlines-hidden)
|
||||
set(PROJECT_INCLUDE ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/include/moveit/task_constructor)
|
||||
|
||||
add_subdirectory(src)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(python)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(test)
|
||||
|
||||
install(DIRECTORY include/ DESTINATION include
|
||||
|
||||
9
core/cmake/pybind11.cmake.in
Normal file
9
core/cmake/pybind11.cmake.in
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
# pybind11 must use the ROS python version
|
||||
set(PYBIND11_PYTHON_VERSION ${PYTHON_VERSION_STRING})
|
||||
|
||||
if(@INSTALLSPACE@)
|
||||
include(${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/pybind11Config.cmake)
|
||||
else()
|
||||
# in build space, directly include pybind11 directory
|
||||
add_subdirectory(${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/../pybind11 ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/pybind11)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
21
core/doc/Doxyfile
Normal file
21
core/doc/Doxyfile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
PROJECT_NAME = MTC
|
||||
INPUT = ../include/ ../src/
|
||||
RECURSIVE = YES
|
||||
|
||||
GENERATE_HTML = YES
|
||||
GENERATE_LATEX = NO
|
||||
GENERATE_XML = NO
|
||||
HTML_OUTPUT = _cpp
|
||||
XML_OUTPUT = _doxygenxml
|
||||
XML_PROGRAMLISTING = YES
|
||||
|
||||
ALIASES = "rst=\verbatim embed:rst"
|
||||
ALIASES += "endrst=\endverbatim"
|
||||
|
||||
QUIET = YES
|
||||
WARNINGS = YES
|
||||
WARN_IF_UNDOCUMENTED = NO
|
||||
|
||||
EXCLUDE_SYMBOLS = *Private
|
||||
EXCLUDE_SYMBOLS += class_
|
||||
EXCLUDE_SYMBOLS += declval*
|
||||
34
core/doc/_templates/custom-class-template.rst
vendored
Normal file
34
core/doc/_templates/custom-class-template.rst
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
{{ fullname | escape | underline}}
|
||||
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: {{ module }}
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: {{ objname }}
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
:show-inheritance:
|
||||
:inherited-members:
|
||||
:special-members: __len__, __getitem__, __iter__, __call__, __add__, __mul__
|
||||
|
||||
{% block methods %}
|
||||
{% if methods %}
|
||||
.. rubric:: {{ _('Methods') }}
|
||||
|
||||
.. autosummary::
|
||||
:nosignatures:
|
||||
{% for item in methods %}
|
||||
{%- if not item.startswith('_') %}
|
||||
~{{ name }}.{{ item }}
|
||||
{%- endif -%}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% endblock %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% block attributes %}
|
||||
{% if attributes %}
|
||||
.. rubric:: {{ _('Attributes') }}
|
||||
|
||||
.. autosummary::
|
||||
{% for item in attributes %}
|
||||
~{{ name }}.{{ item }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% endblock %}
|
||||
66
core/doc/_templates/custom-module-template.rst
vendored
Normal file
66
core/doc/_templates/custom-module-template.rst
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
{{ fullname | escape | underline}}
|
||||
|
||||
.. automodule:: {{ fullname }}
|
||||
|
||||
{% block attributes %}
|
||||
{% if attributes %}
|
||||
.. rubric:: Module attributes
|
||||
|
||||
.. autosummary::
|
||||
:toctree:
|
||||
{% for item in attributes %}
|
||||
{{ item }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% endblock %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% block functions %}
|
||||
{% if functions %}
|
||||
.. rubric:: {{ _('Functions') }}
|
||||
|
||||
.. autosummary::
|
||||
:toctree:
|
||||
:nosignatures:
|
||||
{% for item in functions %}
|
||||
{{ item }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% endblock %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% block classes %}
|
||||
{% if classes %}
|
||||
.. rubric:: {{ _('Classes') }}
|
||||
|
||||
.. autosummary::
|
||||
:toctree:
|
||||
:template: custom-class-template.rst
|
||||
:nosignatures:
|
||||
{% for item in classes %}
|
||||
{{ item }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% endblock %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% block exceptions %}
|
||||
{% if exceptions %}
|
||||
.. rubric:: {{ _('Exceptions') }}
|
||||
|
||||
.. autosummary::
|
||||
:toctree:
|
||||
{% for item in exceptions %}
|
||||
{{ item }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% endblock %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% block modules %}
|
||||
{% if modules %}
|
||||
.. autosummary::
|
||||
:toctree:
|
||||
:template: custom-module-template.rst
|
||||
:recursive:
|
||||
{% for item in modules %}
|
||||
{{ item }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% endblock %}
|
||||
20
core/doc/api.rst
Normal file
20
core/doc/api.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
.. _sec-api:
|
||||
|
||||
API reference
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
`C++ <_static/index.html>`_
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Python
|
||||
^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
.. autosummary::
|
||||
:toctree: _autosummary
|
||||
:caption: API
|
||||
:recursive:
|
||||
:template: custom-module-template.rst
|
||||
|
||||
moveit.task_constructor
|
||||
pymoveit_mtc.core
|
||||
pymoveit_mtc.stages
|
||||
30
core/doc/basics.rst
Normal file
30
core/doc/basics.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
Basic Concepts
|
||||
==============
|
||||
|
||||
The fundamental idea of MTC is that complex motion planning problems can be composed into a set of simpler subproblems. The top-level planning problem is specified as a Task while all subproblems are specified by Stages. Stages can be arranged in any arbitrary order and hierarchy only limited by the individual stages types. The order in which stages can be arranged is restricted by the direction in which results are passed. There are three possible stages relating to the result flow: generator, propagator, and connector stages:
|
||||
|
||||
.. glossary::
|
||||
|
||||
Generators
|
||||
compute their results independently of their neighbor stages and pass them in both directions, backwards and forwards. An example is an IK sampler for geometric poses where approaching and departing motions (neighbor stages) depend on the solution.
|
||||
|
||||
Propagators
|
||||
receive the result of one neighbor stage, solve a subproblem and then propagate their result to the neighbor on the opposite site. Depending on the implementation, propagating stages can pass solutions forward, backward or in both directions separately. An example is a stage that computes a Cartesian path based on either a start or a goal state.
|
||||
|
||||
Connectors
|
||||
do not propagate any results, but rather attempt to bridge the gap between the resulting states of both neighbors. An example is the computation of a free-motion plan from one given state to another.
|
||||
|
||||
Additional to the order types, there are different hierarchy types allowing to encapsulate subordinate stages. Stages without subordinate stages are called primitive stages, higher-level stages are called container stages. There are three container types:
|
||||
|
||||
.. glossary::
|
||||
|
||||
Wrappers
|
||||
encapsulate a single subordinate stage and modify or filter the results. For example, a filter stage that only accepts solutions of its child stage that satisfy a certain constraint can be realized as a wrapper. Another standard use of this type includes the IK wrapper stage, which generates inverse kinematics solutions based on planning scenes annotated with a pose target property.
|
||||
|
||||
Serial Containers
|
||||
hold a sequence of subordinate stages and only consider end-to-end solutions as results. An example is a picking motion that consists of a sequence of coherent steps.
|
||||
|
||||
Parallel Containers
|
||||
combine set of subordinate stages and can be used for passing the best of alternative results, running fallback solvers or for merging multiple independent solutions. Examples are running alternative planners for a free-motion plan, picking objects with the right hand or with the left hand as a fallback, or moving the arm and opening the gripper at the same time.
|
||||
|
||||
Stages not only support solving motion planning problems. They can also be used for all kinds of state transitions, as for instance modifying the planning scene. Combined with the possibility of using class inheritance it is possible to construct very complex behavior while only relying on a well-structured set of primitive stages.
|
||||
9
core/doc/concepts.rst
Normal file
9
core/doc/concepts.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
.. _sec-concepts:
|
||||
|
||||
Concepts
|
||||
------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. toctree::
|
||||
:maxdepth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
basics
|
||||
243
core/doc/conf.py
Normal file
243
core/doc/conf.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,243 @@
|
||||
# Configuration file for the Sphinx documentation builder.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# This file does only contain a selection of the most common options.
|
||||
# For a full list, refer to: http://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/config
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from lxml import etree
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
DIR = Path(__file__).parent.resolve()
|
||||
|
||||
# If extensions (or modules to document with autodoc) are in another directory,
|
||||
# add these directories to sys.path here. If the directory is relative to the
|
||||
# documentation root, use os.path.abspath to make it absolute, like shown here.
|
||||
# sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('.'))
|
||||
|
||||
# -- General configuration ------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
# If your documentation needs a minimal Sphinx version, state it here.
|
||||
# needs_sphinx = '1.0'
|
||||
|
||||
# Add any Sphinx extension module names here, as strings. They can be
|
||||
# extensions coming with Sphinx (named 'sphinx.ext.*') or your custom
|
||||
# ones.
|
||||
extensions = [
|
||||
"sphinx_copybutton",
|
||||
"sphinx.ext.autodoc",
|
||||
"sphinx.ext.autosummary",
|
||||
"sphinx.ext.intersphinx",
|
||||
"sphinx.ext.napoleon",
|
||||
"sphinx.ext.extlinks",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
autosummary_generate = True
|
||||
autoclass_content = "both" # Add __init__ doc (ie. params) to class summaries
|
||||
html_show_sourcelink = False # Remove 'view source code' from top of page (for html, not python)
|
||||
autodoc_inherit_docstrings = True # If no docstring, inherit from base class
|
||||
set_type_checking_flag = True # Enable 'expensive' imports for sphinx_autodoc_typehints
|
||||
add_module_names = False
|
||||
|
||||
# Add any paths that contain templates here, relative to this directory.
|
||||
templates_path = ["_templates"]
|
||||
|
||||
# The suffix(es) of source filenames.
|
||||
# You can specify multiple suffix as a list of string:
|
||||
# source_suffix = ['.rst', '.md']
|
||||
source_suffix = ".rst"
|
||||
|
||||
# The encoding of source files.
|
||||
# source_encoding = 'utf-8-sig'
|
||||
|
||||
# The master toctree document.
|
||||
master_doc = "index"
|
||||
|
||||
# General information about the project.
|
||||
project = "MoveIt Task Constructor"
|
||||
author = "Michael Görner, Robert Haschke"
|
||||
|
||||
# The version info for the project you're documenting, acts as replacement for
|
||||
# |version| and |release|, also used in various other places throughout the
|
||||
# built documents.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Read version from package.xml
|
||||
xml = etree.parse("../package.xml")
|
||||
version = str(xml.xpath("/package/version/text()")[0])
|
||||
|
||||
# The language for content autogenerated by Sphinx. Refer to documentation
|
||||
# for a list of supported languages.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# This is also used if you do content translation via gettext catalogs.
|
||||
# Usually you set "language" from the command line for these cases.
|
||||
language = "en"
|
||||
|
||||
# There are two options for replacing |today|: either, you set today to some
|
||||
# non-false value, then it is used:
|
||||
# today = ''
|
||||
# Else, today_fmt is used as the format for a strftime call.
|
||||
# today_fmt = '%B %d, %Y'
|
||||
|
||||
# List of patterns, relative to source directory, that match files and
|
||||
# directories to ignore when looking for source files.
|
||||
exclude_patterns = [".build", "python/pybind11"]
|
||||
|
||||
# The reST default role (used for this markup: `text`) to use for all
|
||||
# documents.
|
||||
# default_role = None
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, '()' will be appended to :func: etc. cross-reference text.
|
||||
# add_function_parentheses = True
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, the current module name will be prepended to all description
|
||||
# unit titles (such as .. function::).
|
||||
# add_module_names = True
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, sectionauthor and moduleauthor directives will be shown in the
|
||||
# output. They are ignored by default.
|
||||
# show_authors = False
|
||||
|
||||
# The name of the Pygments (syntax highlighting) style to use.
|
||||
# pygments_style = 'monokai'
|
||||
|
||||
# A list of ignored prefixes for module index sorting.
|
||||
# modindex_common_prefix = []
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, keep warnings as "system message" paragraphs in the built documents.
|
||||
# keep_warnings = False
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, `todo` and `todoList` produce output, else they produce nothing.
|
||||
todo_include_todos = False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -- Options for HTML output ----------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
# The theme to use for HTML and HTML Help pages. See the documentation for
|
||||
# a list of builtin themes.
|
||||
html_theme = "furo"
|
||||
|
||||
# Theme options are theme-specific and customize the look and feel of a theme
|
||||
# further. For a list of options available for each theme, see the
|
||||
# documentation.
|
||||
# html_theme_options = {}
|
||||
|
||||
# Add any paths that contain custom themes here, relative to this directory.
|
||||
# html_theme_path = []
|
||||
|
||||
# The name for this set of Sphinx documents. If None, it defaults to
|
||||
# "<project> v<release> documentation".
|
||||
# html_title = None
|
||||
|
||||
# A shorter title for the navigation bar. Default is the same as html_title.
|
||||
# html_short_title = None
|
||||
|
||||
# The name of an image file (relative to this directory) to place at the top
|
||||
# of the sidebar.
|
||||
# html_logo = None
|
||||
|
||||
# The name of an image file (within the static path) to use as favicon of the
|
||||
# docs. This file should be a Windows icon file (.ico) being 16x16 or 32x32
|
||||
# pixels large.
|
||||
# html_favicon = None
|
||||
|
||||
# Add any paths that contain custom static files (such as style sheets) here,
|
||||
# relative to this directory. They are copied after the builtin static files,
|
||||
# so a file named "default.css" will overwrite the builtin "default.css".
|
||||
html_static_path = ["_cpp"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Add any extra paths that contain custom files (such as robots.txt or
|
||||
# .htaccess) here, relative to this directory. These files are copied
|
||||
# directly to the root of the documentation.
|
||||
# html_extra_path = []
|
||||
|
||||
# If not '', a 'Last updated on:' timestamp is inserted at every page bottom,
|
||||
# using the given strftime format.
|
||||
# html_last_updated_fmt = '%b %d, %Y'
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, SmartyPants will be used to convert quotes and dashes to
|
||||
# typographically correct entities.
|
||||
# html_use_smartypants = True
|
||||
|
||||
# Custom sidebar templates, maps document names to template names.
|
||||
# html_sidebars = {}
|
||||
|
||||
# Additional templates that should be rendered to pages, maps page names to
|
||||
# template names.
|
||||
# html_additional_pages = {}
|
||||
|
||||
# If false, no module index is generated.
|
||||
# html_domain_indices = True
|
||||
|
||||
# If false, no index is generated.
|
||||
# html_use_index = True
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, the index is split into individual pages for each letter.
|
||||
# html_split_index = False
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, links to the reST sources are added to the pages.
|
||||
# html_show_sourcelink = True
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, "Created using Sphinx" is shown in the HTML footer. Default is True.
|
||||
# html_show_sphinx = True
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, "(C) Copyright ..." is shown in the HTML footer. Default is True.
|
||||
# html_show_copyright = True
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, an OpenSearch description file will be output, and all pages will
|
||||
# contain a <link> tag referring to it. The value of this option must be the
|
||||
# base URL from which the finished HTML is served.
|
||||
# html_use_opensearch = ''
|
||||
|
||||
# This is the file name suffix for HTML files (e.g. ".xhtml").
|
||||
# html_file_suffix = None
|
||||
|
||||
# Language to be used for generating the HTML full-text search index.
|
||||
# Sphinx supports the following languages:
|
||||
# html_search_language = 'en'
|
||||
|
||||
# A dictionary with options for the search language support, empty by default.
|
||||
# Now only 'ja' uses this config value
|
||||
# html_search_options = {'type': 'default'}
|
||||
|
||||
# The name of a javascript file (relative to the configuration directory) that
|
||||
# implements a search results scorer. If empty, the default will be used.
|
||||
# html_search_scorer = 'scorer.js'
|
||||
|
||||
# Output file base name for HTML help builder.
|
||||
htmlhelp_basename = "mtcdoc"
|
||||
|
||||
# Example configuration for intersphinx: refer to the Python standard library.
|
||||
intersphinx_mapping = {"python": ("https://docs.python.org/3", None)}
|
||||
|
||||
ros_distro = "noetic"
|
||||
ros_docs = f"http://docs.ros.org/{ros_distro}/api"
|
||||
extlinks = {
|
||||
"rosdocs": (f"{ros_docs}/%s", "%s"),
|
||||
"msgs": (f"{ros_docs}/moveit_task_constructor/html/msg/%s.html", "%s"),
|
||||
"moveit_msgs": (f"{ros_docs}/moveit_msgs/html/msg/%s.html", "%s"),
|
||||
"geometry_msgs": (f"{ros_docs}/geometry_msgs/html/msg/%s.html", "%s"),
|
||||
"visualization_msgs": (f"{ros_docs}/visualization_msgs/html/msg/%s.html", "%s"),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def generate_doxygen_xml(app):
|
||||
build_dir = os.path.join(app.confdir, ".build")
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(build_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(build_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Running doxygen")
|
||||
try:
|
||||
subprocess.call(["doxygen", "--version"])
|
||||
retcode = subprocess.call(["doxygen"], cwd=app.confdir)
|
||||
if retcode < 0:
|
||||
sys.stderr.write(f"doxygen error code: {-retcode}\n")
|
||||
except OSError as e:
|
||||
sys.stderr.write(f"doxygen execution failed: {e}\n")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def setup(app):
|
||||
# Add hook for building doxygen xml when needed
|
||||
# app.connect("builder-inited", generate_doxygen_xml)
|
||||
pass
|
||||
301
core/doc/howto.rst
Normal file
301
core/doc/howto.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,301 @@
|
||||
.. _sec-howtoguides:
|
||||
|
||||
How-To Guides
|
||||
=============
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsec-howto-stage-usage:
|
||||
|
||||
Stage Usage
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-alternatives:
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatives
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Using the ``alternatives`` stage, you can plan for multiple
|
||||
execution paths.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/alternatives.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/alternatives.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigAlternatives]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigAlternatives]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-fallbacks:
|
||||
|
||||
Fallbacks
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
The ``fallbacks`` stage provides alternative motion planners
|
||||
if planning fails with the primary one.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/fallbacks.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/fallbacks.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigFallbacks]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigFallbacks]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-merger:
|
||||
|
||||
Merger
|
||||
^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Plan and execute sequences in parallel using the ``merger`` stage.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/merger.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/merger.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigMerger]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigMerger]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-connect:
|
||||
|
||||
Connect
|
||||
^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Connect two stages by finding a motion plan between them.
|
||||
The code snippet is part of the :ref:`Pick and Place <subsec-tut-pick-place>` guide.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigConnect]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigConnect]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-fix-collision-objects:
|
||||
|
||||
FixCollisionObjects
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Check for collisions and resolve them if applicable.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/fix_collision_objects.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/fix_collision_objects.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfig]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfig]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-generate-place-pose:
|
||||
|
||||
GeneratePlacePose
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Sample feasible poses around an object pose.
|
||||
Considers geometry of primitive object type.
|
||||
Solutions can be used for inverse
|
||||
kinematics calculations.
|
||||
The code snippet is part of the :ref:`Pick and Place <subsec-tut-pick-place>` guide.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initCollisionObject]
|
||||
:end-before: [initCollisionObject]
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigGeneratePlacePose]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigGeneratePlacePose]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-generate-grasp-pose:
|
||||
|
||||
GenerateGraspPose
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Sample poses around an object pose by providing
|
||||
sample density ``angle_delta``.
|
||||
Solutions can be used for inverse kinematics
|
||||
calculations.
|
||||
The code snippet is part of the :ref:`Pick and Place <subsec-tut-pick-place>` guide.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigGenerateGraspPose]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigGenerateGraspPose]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-generate-pose:
|
||||
|
||||
GeneratePose
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Spawn a pose on new solutions of the monitored stage.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/generate_pose.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/generate_pose.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigGeneratePose]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigGeneratePose]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-pick:
|
||||
|
||||
Pick
|
||||
^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Wraps the task pipeline to execute a pick.
|
||||
The code snippet is part of the :ref:`Pick and Place <subsec-tut-pick-place>` guide.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigPick]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigPick]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-place:
|
||||
|
||||
Place
|
||||
^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Wraps the task pipeline to execute a pick.
|
||||
The code snippet is part of the :ref:`Pick and Place <subsec-tut-pick-place>` guide.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigPlace]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigPlace]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-simplegrasp:
|
||||
|
||||
SimpleGrasp
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Wraps the pose generation and inverse kinematics
|
||||
computation for the pick pipeline.
|
||||
The code snippet is part of the :ref:`Pick and Place <subsec-tut-pick-place>` guide.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigSimpleGrasp]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigSimpleGrasp]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-simpleungrasp:
|
||||
|
||||
SimpleUnGrasp
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Wraps the pose generation and inverse kinematics
|
||||
computation for the place pipeline.
|
||||
The code snippet is part of the :ref:`Pick and Place <subsec-tut-pick-place>` guide.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigSimpleUnGrasp]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigSimpleUnGrasp]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-modify-planning-scene:
|
||||
|
||||
ModifyPlanningScene
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Modify the planning scene.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/modify_planning_scene.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/modify_planning_scene.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigModifyPlanningScene]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigModifyPlanningScene]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-fixed-state:
|
||||
|
||||
FixedState
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Spawn a pre-defined state.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/fixed_state.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/fixed_state.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigFixedState]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigFixedState]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-compute-ik:
|
||||
|
||||
ComputeIK
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Compute the inverse kinematics of the monitored stages'
|
||||
solution. Be sure to correctly configure the ``target_pose``
|
||||
property to be derived from the monitored stage as shown
|
||||
in the example.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <./../../demo/scripts/compute_ik.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../demo/scripts/compute_ik.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigComputeIk]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigComputeIk]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-move-to:
|
||||
|
||||
MoveTo
|
||||
^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Use planners to compute a motion plan.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigMoveTo]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigMoveTo]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-move-relative:
|
||||
|
||||
MoveRelative
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Move along a relative offset.
|
||||
Download the full example code here: :download:`Source <../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigMoveRelative]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigMoveRelative]
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsec-howto-stage-extension:
|
||||
|
||||
Stage Extension
|
||||
---------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-move-relative-extension:
|
||||
|
||||
MoveRelative
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
You may derive from this stage to extend its functionality.
|
||||
``MoveRelative`` itself derives from the propagator stage that
|
||||
alters solutions (i.e. computes a motion plan) when they are
|
||||
passed through the stage.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../core/python/test/rostest_trampoline.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:pyobject: PyMoveRelX
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-generator-extension:
|
||||
|
||||
Generator
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Derive from the ``Generator`` stage to implement your own
|
||||
logic in the compute function.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../core/python/test/rostest_trampoline.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:pyobject: PyGenerator
|
||||
|
||||
.. _subsubsec-howto-monitoring-generator-extension:
|
||||
|
||||
MonitoringGenerator
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Derive from the ``MonitoringGenerator`` stage to
|
||||
implement your own logic in the compute function.
|
||||
Use the monitoring generator instead of the normal
|
||||
generator if you need to access solutions of the
|
||||
monitored stage (e.g. computation of inverse kinematics).
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../core/python/test/rostest_trampoline.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:pyobject: PyMonitoringGenerator
|
||||
30
core/doc/index.rst
Normal file
30
core/doc/index.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
MoveIt Task Constructor (MTC)
|
||||
=============================
|
||||
|
||||
The Task Constructor framework provides a flexible and transparent way
|
||||
to define and plan actions that consist of multiple interdependent subtasks.
|
||||
It draws on the planning capabilities of MoveIt to solve individual subproblems
|
||||
in black-box planning stages.
|
||||
A common interface, based on MoveIt’s PlanningScene is used to pass solution
|
||||
hypotheses between stages. The framework enables the hierarchical organization of
|
||||
basic stages using containers, allowing for sequential as well as parallel compositions.
|
||||
For more details, please refer to the associated `ICRA 2019 publication <https://pub.uni-bielefeld.de/download/2918864/2933599/paper.pdf>`_.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Organization of the documentation
|
||||
---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- :ref:`sec-tutorials` provide examples how to setup your task pipeline.
|
||||
Start with :ref:`subsec-tut-firststeps` if you are new to MTC.
|
||||
- :ref:`sec-concepts` discuss the architecture and terminology of MTC on a fairly high level.
|
||||
- :ref:`sec-howtoguides` help solving specific problems and use cases.
|
||||
- The :ref:`sec-api` provides quick access to available classes, functions, and their parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
.. toctree::
|
||||
:maxdepth: 2
|
||||
:hidden:
|
||||
|
||||
tutorials/index
|
||||
concepts
|
||||
howto
|
||||
api
|
||||
4
core/doc/requirements.txt
Normal file
4
core/doc/requirements.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
furo
|
||||
lxml
|
||||
sphinx
|
||||
sphinx-copybutton
|
||||
86
core/doc/tutorials/cartesian.rst
Normal file
86
core/doc/tutorials/cartesian.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
.. _subsec-tut-cartesian:
|
||||
|
||||
Cartesian
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
The following example demonstrates how to compute a simple point to point motion
|
||||
plan using the moveit task constructor. You can take a look at the full
|
||||
source code here:
|
||||
:download:`Source <../../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py>`
|
||||
|
||||
First, lets make sure we specify the planning group and the
|
||||
end effector that we want to use.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [cartesianTut1]
|
||||
:end-before: [cartesianTut1]
|
||||
|
||||
The moveit task constructor provides different planners.
|
||||
We will use the ``CartesianPath`` and ``JointInterpolation``
|
||||
planners for this example.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [cartesianTut2]
|
||||
:end-before: [cartesianTut2]
|
||||
|
||||
Lets start by initializing a task and adding the current
|
||||
planning scene state and robot state to it.
|
||||
This will be the starting state for our motion plan.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [cartesianTut3]
|
||||
:end-before: [cartesianTut3]
|
||||
|
||||
To compute a relative motion in cartesian space, we can use
|
||||
the ``MoveRelative`` stage. Specify the planning group and
|
||||
frame relative to which you want to carry out the motion.
|
||||
the relative direction can be specified by a ``Vector3Stamped``
|
||||
geometry message.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigMoveRelative]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigMoveRelative]
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly we can move along a different axis.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [cartesianTut4]
|
||||
:end-before: [cartesianTut4]
|
||||
|
||||
The ``MoveRelative`` stage also offers an interface to
|
||||
``Twist`` messages, allowing to specify rotations.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [cartesianTut5]
|
||||
:end-before: [cartesianTut5]
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, we can compute linear movements in cartesian space
|
||||
by providing offsets in joint space.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [cartesianTut6]
|
||||
:end-before: [cartesianTut6]
|
||||
|
||||
If we want to specify goals instead of directions,
|
||||
we can use the ``MoveTo`` stage. In the following example
|
||||
we use simple joint interpolation to move the robot to
|
||||
a named pose. the named pose is defined in the urdf of
|
||||
the robot configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/cartesian.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [initAndConfigMoveTo]
|
||||
:end-before: [initAndConfigMoveTo]
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, we invoke the planning mechanism that traverses
|
||||
the task hierarchy for us and compute a valid motion plan.
|
||||
At this point, when you run this script you are able to
|
||||
inspect the solutions of the individual stages in the rviz
|
||||
mtc panel.
|
||||
22
core/doc/tutorials/first-steps.rst
Normal file
22
core/doc/tutorials/first-steps.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
.. _subsec-tut-firststeps:
|
||||
|
||||
First Steps
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
The MoveIt Task Constructor package contains several basic examples and
|
||||
a pick-and-place demo. For all demos you should launch the basic environment:
|
||||
|
||||
.. code-block::
|
||||
|
||||
roslaunch moveit_task_constructor_demo demo.launch
|
||||
|
||||
Subsequently, you can run the individual demos:
|
||||
|
||||
.. code-block::
|
||||
|
||||
rosrun moveit_task_constructor_demo cartesian
|
||||
rosrun moveit_task_constructor_demo modular
|
||||
roslaunch moveit_task_constructor_demo pickplace.launch
|
||||
|
||||
To inspect the task hierarchy, be sure that you selected the correct solution topic
|
||||
in the reviz moveit task constructor plugin.
|
||||
15
core/doc/tutorials/index.rst
Normal file
15
core/doc/tutorials/index.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
.. _sec-tutorials:
|
||||
|
||||
Tutorials
|
||||
=========
|
||||
|
||||
The following tutorials take you step by step through the implementation of fundamental examples
|
||||
of the moveit task constructor.
|
||||
|
||||
.. toctree::
|
||||
:caption: Tutorials
|
||||
|
||||
first-steps
|
||||
cartesian
|
||||
properties
|
||||
pick-and-place
|
||||
138
core/doc/tutorials/pick-and-place.rst
Normal file
138
core/doc/tutorials/pick-and-place.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
|
||||
.. _subsec-tut-pick-place:
|
||||
|
||||
Pick and Place
|
||||
--------------
|
||||
|
||||
The following tutorial demonstrates how you can use the moveit
|
||||
task constructor to plan and carry out pick and place movements.
|
||||
|
||||
First, lets specify the planning group and the
|
||||
end effector that you want to use.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut1]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut1]
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we add the object that we want to displace to the
|
||||
planning scene. To this end, make sure that the planning scene
|
||||
not already contains such object.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut2]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut2]
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, we are ready to create the task hierarchy.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut3]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut3]
|
||||
|
||||
The pipeline planner encapsulates the moveit interface
|
||||
to sampling-based geometric motion planners.
|
||||
|
||||
.. tip::
|
||||
Planning does not proceed linearly from top to bottom.
|
||||
Rather, it proceeds from the inside out.
|
||||
Connect stages therefore compute a motion plan between
|
||||
two previously calculated subordinate solutions.
|
||||
For a clear visualization, inspect the rviz mtc panel.
|
||||
|
||||
Lets connect the current robot state with the solutions of
|
||||
the following stages.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut4]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut4]
|
||||
|
||||
To pick the object, we first need to know possible end effector
|
||||
poses with which we can perform a successful grasp.
|
||||
For this, we use a ``GenerateGraspPoseStage``.
|
||||
which essentially spawns poses
|
||||
with a given ``angle_delta`` in circular fashion around a center
|
||||
point.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut5]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut5]
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we need to compute the inverse kinematics of the robot arm
|
||||
for all previously sampled poses. This way we can
|
||||
rule out solutions that are not feasible due to the robot geometry.
|
||||
The ``simpleGrasp`` stage combines ik calculation with motion plan
|
||||
generation for opening and closing the end effector, as well as attaching
|
||||
the object to the robot an disabling collision.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut6]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut6]
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, we can insert all the previous steps into the ``Pick``
|
||||
container stage. At this point we might also specify approach and
|
||||
lift twists for the robot relative to the object we want to grasp.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut7]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut7]
|
||||
|
||||
Since all the previous stages were chained together via their
|
||||
constructor arguments, we only need to add the top level ``Pick``
|
||||
stage to the task hierarchy.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut8]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut8]
|
||||
|
||||
Thats everything we need for picking an object!
|
||||
Lets find a motion plan to place the object
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut9]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut9]
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to the picking procedure, we define the place task.
|
||||
First, start with sampling place poses.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut10]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut10]
|
||||
|
||||
Next, wrap the inverse kinematics computation and gripper
|
||||
movements.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut11]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut11]
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, add place and retract motions and add the ``Place``
|
||||
stage to the task hierarchy.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut12]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut12]
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, compute solutions for the task hierarchy and delete
|
||||
the planner instances.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/pickplace.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [pickAndPlaceTut13]
|
||||
:end-before: [pickAndPlaceTut13]
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, you might inspect the task hierarchy in the mtc rviz
|
||||
plugin.
|
||||
|
||||
.. tip::
|
||||
Use the mtc rviz plugin to graphically inspect the solutions
|
||||
of individual stages in the task hierarchy.
|
||||
127
core/doc/tutorials/properties.rst
Normal file
127
core/doc/tutorials/properties.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
||||
.. _subsec-tut-properties:
|
||||
|
||||
Properties
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Properties are named attributes of a stage.
|
||||
They can be used to configure the stages behaviour
|
||||
and control further substages. Lets take a closer
|
||||
look at how to work with properties.
|
||||
|
||||
Basic Operations with Properties
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
Lets define a property and assign a description, as well as
|
||||
a value to it.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/properties.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut1]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut1]
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that a property always has two values: the current value
|
||||
and the default value. Before we use the property, we might want to
|
||||
check if the current value defined.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/properties.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut2]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut2]
|
||||
|
||||
Now we are ready to safely retrieve the values of the proprty!
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/properties.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut3]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut3]
|
||||
|
||||
The Property Map
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Usually a stage comprises multiple properties. A stage
|
||||
contains a single PropertyMap that acts as a container for
|
||||
all properties associated to that stage.
|
||||
|
||||
Lets first create a PropertyMap in isolation and initialize
|
||||
some properties using a dict. As you can see, properties can be
|
||||
of arbitrary type.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/properties.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut4]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut4]
|
||||
|
||||
Properties can also be initialized using a more pythonic way.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/properties.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut5]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut5]
|
||||
|
||||
There are two ways to retrieve properties back from the property map.
|
||||
We might only be interested in in the value of the property:
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/properties.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut6]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut6]
|
||||
|
||||
Or we can obtain a reference to the whole property object.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/properties.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut7]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut7]
|
||||
|
||||
The PropertyMap class additionally provides an iterator that can be used in loops.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/properties.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut8]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut8]
|
||||
|
||||
Remember that wer initialized our PropertyMap by using a dict. In fact, you
|
||||
can also use an existing PropertMap to copy over some properties.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/properties.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut9]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut9]
|
||||
|
||||
Accessing Properties of a Stage
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
You can obtain a reference to the the PropertyMap of a stage like so
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/properties.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut10]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut10]
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/properties.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut11]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut11]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned, each stage contains a PropertyMap.
|
||||
Stages communicate to each other via their interfaces.
|
||||
If you want to forward properties through these interfaces,
|
||||
you can use the reference of a stages' property object.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/compute_ik.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut12]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut12]
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/compute_ik.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut13]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut13]
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ../../../demo/scripts/compute_ik.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
:start-after: [propertyTut14]
|
||||
:end-before: [propertyTut14]
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-compute-ik>`
|
||||
for a full example of this.
|
||||
27
core/include/moveit/python/python_tools/geometry_msg_types.h
Normal file
27
core/include/moveit/python/python_tools/geometry_msg_types.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
#pragma once
|
||||
|
||||
#include "ros_types.h"
|
||||
#include <geometry_msgs/PoseStamped.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/** Convienency type casters, also allowing to initialize Stamped geometry msgs from a string */
|
||||
|
||||
namespace pybind11 {
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <>
|
||||
struct type_caster<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> : type_caster_ros_msg<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Python -> C++
|
||||
bool load(handle src, bool convert) {
|
||||
type_caster<std::string> str_caster;
|
||||
if (convert && str_caster.load(src, false)) { // string creates identity pose with given frame
|
||||
value.header.frame_id = static_cast<std::string&>(str_caster);
|
||||
value.pose.orientation.w = 1.0;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return type_caster_ros_msg<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>::load(src, convert);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
} // namespace pybind11
|
||||
31
core/include/moveit/python/python_tools/ros_init.h
Normal file
31
core/include/moveit/python/python_tools/ros_init.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
#pragma once
|
||||
|
||||
#include <memory>
|
||||
#include <boost/thread/mutex.hpp>
|
||||
#include <ros/spinner.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace python {
|
||||
|
||||
/// singleton class to initialize ROS C++ (once) from Python
|
||||
class InitProxy
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static void init(const std::string& node_name = "moveit_python_wrapper",
|
||||
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& remappings = std::map<std::string, std::string>(),
|
||||
uint32_t options = 0);
|
||||
static void shutdown();
|
||||
|
||||
~InitProxy();
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
InitProxy(const std::string& node_name, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& remappings, uint32_t options);
|
||||
|
||||
static boost::mutex lock_;
|
||||
static std::unique_ptr<InitProxy> singleton_instance_;
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<ros::AsyncSpinner> spinner;
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace python
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
90
core/include/moveit/python/python_tools/ros_types.h
Normal file
90
core/include/moveit/python/python_tools/ros_types.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
||||
#pragma once
|
||||
|
||||
#include <pybind11/smart_holder.h>
|
||||
#include <rclcpp/duration.hpp>
|
||||
#include <rclcpp/serialization.hpp>
|
||||
|
||||
/** Provide pybind11 type converters for ROS types */
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace python {
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_EXPORT pybind11::object createMessage(const std::string& ros_msg_name);
|
||||
PYBIND11_EXPORT bool convertible(const pybind11::handle& h, const char* ros_msg_name);
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace python
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
|
||||
namespace pybind11 {
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
/// Convert ros::Duration / ros::WallDuration into a float
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct DurationCaster
|
||||
{
|
||||
// C++ -> Python
|
||||
static handle cast(T&& src, return_value_policy /* policy */, handle /* parent */) {
|
||||
return PyFloat_FromDouble(src.toSec());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Python -> C++
|
||||
bool load(handle src, bool convert) {
|
||||
if (hasattr(src, "to_sec")) {
|
||||
value = T(src.attr("to_sec")().cast<double>());
|
||||
} else if (convert) {
|
||||
value = T(src.cast<double>());
|
||||
} else
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(T, _("Duration"));
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <>
|
||||
struct type_caster<rclcpp::Duration> : DurationCaster<rclcpp::Duration>
|
||||
{};
|
||||
|
||||
/// Convert ROS message types (C++ <-> python)
|
||||
template <typename T, typename SFINAE = enable_if_t<ros::message_traits::IsMessage<T>::value>>
|
||||
struct type_caster_ros_msg
|
||||
{
|
||||
// C++ -> Python
|
||||
static handle cast(const T& src, return_value_policy /* policy */, handle /* parent */) {
|
||||
// serialize src into (python) buffer
|
||||
std::size_t size = ros::serialization::serializationLength(src);
|
||||
object pbuffer = reinterpret_steal<object>(PyBytes_FromStringAndSize(nullptr, size));
|
||||
ros::serialization::OStream stream(reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(PyBytes_AsString(pbuffer.ptr())), size);
|
||||
ros::serialization::serialize(stream, src);
|
||||
// deserialize python type from buffer
|
||||
object msg = moveit::python::createMessage(ros::message_traits::DataType<T>::value());
|
||||
msg.attr("deserialize")(pbuffer);
|
||||
return msg.release();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Python -> C++
|
||||
bool load(handle src, bool /*convert*/) {
|
||||
if (!moveit::python::convertible(src, ros::message_traits::DataType<T>::value()))
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
// serialize src into (python) buffer
|
||||
object pstream = module::import("io").attr("BytesIO")();
|
||||
src.attr("serialize")(pstream);
|
||||
object pbuffer = pstream.attr("getvalue")();
|
||||
// deserialize C++ type from buffer
|
||||
char* cbuffer = nullptr;
|
||||
Py_ssize_t size;
|
||||
PyBytes_AsStringAndSize(pbuffer.ptr(), &cbuffer, &size);
|
||||
ros::serialization::IStream cstream(const_cast<uint8_t*>(reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(cbuffer)), size);
|
||||
ros::serialization::deserialize(cstream, value);
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(T, _<T>());
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct type_caster<T, enable_if_t<ros::message_traits::IsMessage<T>::value>> : type_caster_ros_msg<T>
|
||||
{};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
} // namespace pybind11
|
||||
78
core/include/moveit/python/task_constructor/properties.h
Normal file
78
core/include/moveit/python/task_constructor/properties.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
||||
#pragma once
|
||||
|
||||
#include <moveit/python/python_tools/ros_types.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/python/python_tools/geometry_msg_types.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/properties.h>
|
||||
#include <boost/any.hpp>
|
||||
#include <typeindex>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace python {
|
||||
|
||||
class PYBIND11_EXPORT PropertyConverterBase
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using to_python_converter_function = pybind11::object (*)(const boost::any&);
|
||||
using from_python_converter_function = boost::any (*)(const pybind11::object&);
|
||||
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
static bool insert(const std::type_index& type_index, const std::string& ros_msg_name,
|
||||
to_python_converter_function to, from_python_converter_function from);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/// utility class to register C++ / Python converters for a property of type T
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
class PropertyConverter : protected PropertyConverterBase
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
PropertyConverter() { insert(typeid(T), rosMsgName<T>(), &toPython, &fromPython); }
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
static pybind11::object toPython(const boost::any& value) { return pybind11::cast(boost::any_cast<T>(value)); }
|
||||
static boost::any fromPython(const pybind11::object& po) { return pybind11::cast<T>(po); }
|
||||
|
||||
template <class Q = T>
|
||||
typename std::enable_if<ros::message_traits::IsMessage<Q>::value, std::string>::type rosMsgName() {
|
||||
return ros::message_traits::DataType<T>::value();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <class Q = T>
|
||||
typename std::enable_if<!ros::message_traits::IsMessage<Q>::value, std::string>::type rosMsgName() {
|
||||
return std::string();
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace properties {
|
||||
|
||||
/** Extension for pybind11::class_ to allow convienient definition of properties
|
||||
*
|
||||
* New method property<PropertyType>(const char* name) adds a property getter/setter.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename type_, typename... options>
|
||||
class class_ : public pybind11::classh<type_, options...> // NOLINT(readability-identifier-naming)
|
||||
{
|
||||
using base_class_ = pybind11::classh<type_, options...>;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
// forward all constructors
|
||||
using base_class_::classh;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename PropertyType, typename... Extra>
|
||||
class_& property(const char* name, const Extra&... extra) {
|
||||
PropertyConverter<PropertyType>(); // register corresponding property converter
|
||||
auto getter = [name](const type_& self) {
|
||||
const moveit::task_constructor::PropertyMap& props = self.properties();
|
||||
return props.get<PropertyType>(name);
|
||||
};
|
||||
auto setter = [name](type_& self, const PropertyType& value) {
|
||||
moveit::task_constructor::PropertyMap& props = self.properties();
|
||||
props.set(name, boost::any(value));
|
||||
};
|
||||
base_class_::def_property(name, getter, setter, pybind11::return_value_policy::reference_internal, extra...);
|
||||
return *this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace properties
|
||||
} // namespace python
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
@ -53,6 +53,7 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
size_t numChildren() const;
|
||||
Stage* findChild(const std::string& name) const;
|
||||
Stage* operator[](int index) const;
|
||||
|
||||
/** Callback function type used by traverse functions
|
||||
* Receives currently visited Stage and current depth in hierarchy
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,6 +40,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/storage.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/utils.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit_msgs/msg/robot_state.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace task_constructor {
|
||||
@ -69,6 +70,14 @@ public:
|
||||
class TrajectoryCostTerm : public CostTerm
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
enum class Mode
|
||||
{
|
||||
AUTO /* TRAJECTORY, or START_INTERFACE if no trajectory is given */,
|
||||
START_INTERFACE,
|
||||
END_INTERFACE,
|
||||
TRAJECTORY
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
double operator()(const SolutionSequence& s, std::string& comment) const override;
|
||||
double operator()(const WrappedSolution& s, std::string& comment) const override;
|
||||
};
|
||||
@ -113,15 +122,34 @@ public:
|
||||
double cost;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/// trajectory length (interpolated between waypoints)
|
||||
/// trajectory length with optional weighting for different joints
|
||||
class PathLength : public TrajectoryCostTerm
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
/// By default, all joints are considered with same weight of 1.0
|
||||
PathLength() = default;
|
||||
PathLength(std::vector<std::string> j) : joints{ std::move(j) } {};
|
||||
/// Limit measurements to given joint names
|
||||
PathLength(std::vector<std::string> joints);
|
||||
/// Limit measurements to given joints and use given weighting
|
||||
PathLength(std::map<std::string, double> j) : joints(std::move(j)) {}
|
||||
double operator()(const SubTrajectory& s, std::string& comment) const override;
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<std::string> joints;
|
||||
std::map<std::string, double> joints; //< joint weights
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/// (weighted) joint-space distance to reference pose
|
||||
class DistanceToReference : public TrajectoryCostTerm
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
DistanceToReference(const moveit_msgs::msg::RobotState& ref, Mode m = Mode::AUTO,
|
||||
std::map<std::string, double> w = std::map<std::string, double>());
|
||||
DistanceToReference(const std::map<std::string, double>& ref, Mode m = Mode::AUTO,
|
||||
std::map<std::string, double> w = std::map<std::string, double>());
|
||||
double operator()(const SubTrajectory& s, std::string& comment) const override;
|
||||
|
||||
moveit_msgs::msg::RobotState reference;
|
||||
std::map<std::string, double> weights;
|
||||
Mode mode;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/// execution duration of the whole trajectory
|
||||
@ -153,14 +181,6 @@ public:
|
||||
class Clearance : public TrajectoryCostTerm
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
enum class Mode
|
||||
{
|
||||
AUTO /* TRAJECTORY, or START_INTERFACE if no trajectory is given */,
|
||||
START_INTERFACE,
|
||||
END_INTERFACE,
|
||||
TRAJECTORY
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
Clearance(bool with_world = true, bool cumulative = false, std::string group_property = "group",
|
||||
Mode mode = Mode::AUTO);
|
||||
bool with_world;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -96,8 +96,8 @@ public:
|
||||
void publishAllSolutions(bool wait = true);
|
||||
|
||||
/// get solution
|
||||
bool getSolution(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::srv::GetSolution::Request::SharedPtr req,
|
||||
const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::srv::GetSolution::Response::SharedPtr res);
|
||||
bool getSolution(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::srv::GetSolution::Request::SharedPtr& req,
|
||||
const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::srv::GetSolution::Response::SharedPtr& res);
|
||||
|
||||
/// retrieve id of given stage
|
||||
uint32_t stageId(const moveit::task_constructor::Stage* const s) const;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -291,8 +291,8 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
// Default implementations, using generic compute().
|
||||
// Override if you want to use different code for FORWARD and BACKWARD directions.
|
||||
virtual void computeForward(const InterfaceState& from) { computeGeneric<Interface::FORWARD>(from); }
|
||||
virtual void computeBackward(const InterfaceState& to) { computeGeneric<Interface::BACKWARD>(to); }
|
||||
virtual void computeForward(const InterfaceState& from);
|
||||
virtual void computeBackward(const InterfaceState& to);
|
||||
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
// constructor for use in derived classes
|
||||
|
||||
@ -80,13 +80,12 @@ public:
|
||||
/// set properties of IK solver
|
||||
void setIKFrame(const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped& transform) { setProperty("ik_frame", transform); }
|
||||
void setIKFrame(const Eigen::Isometry3d& pose, const std::string& link);
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
void setIKFrame(const T& t, const std::string& link) {
|
||||
Eigen::Isometry3d transform;
|
||||
transform = t;
|
||||
setIKFrame(transform, link);
|
||||
}
|
||||
void setIKFrame(const std::string& link) { setIKFrame(Eigen::Isometry3d::Identity(), link); }
|
||||
/// allow setting IK frame from any type T that converts to Eigen::Isometry3d
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
void setIKFrame(const T& transform, const std::string& link) {
|
||||
setIKFrame(Eigen::Isometry3d(transform), link);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void setMaxIKSolutions(uint32_t max_ik_solutions) { setProperty("max_ik_solutions", max_ik_solutions); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ public:
|
||||
ARMED, // disabled state in a Connecting interface that will become re-enabled with a new opposite state
|
||||
PRUNED, // disabled state on a pruned solution branch
|
||||
};
|
||||
static const char* STATUS_COLOR[];
|
||||
static const char* colorForStatus(unsigned int s) { return STATUS_COLOR_[s]; }
|
||||
|
||||
/** InterfaceStates are ordered according to two values:
|
||||
* Depth of interlinked trajectory parts and accumulated trajectory costs along that path.
|
||||
@ -158,6 +158,7 @@ private:
|
||||
inline void setPriority(const Priority& prio) { priority_ = prio; }
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
static const char* STATUS_COLOR_[];
|
||||
planning_scene::PlanningSceneConstPtr scene_;
|
||||
PropertyMap properties_;
|
||||
/// trajectories which are *timewise before* this state
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,6 +75,8 @@ class Task : protected WrapperBase
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
PRIVATE_CLASS(Task)
|
||||
using WrapperBase::setCostTerm;
|
||||
using WrapperBase::operator[];
|
||||
|
||||
Task(const std::string& ns = "", bool introspection = true,
|
||||
ContainerBase::pointer&& container = std::make_unique<SerialContainer>("task pipeline"));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,13 +1,18 @@
|
||||
<package format="2">
|
||||
<package format="3">
|
||||
<name>moveit_task_constructor_core</name>
|
||||
<version>0.0.0</version>
|
||||
<description>MoveIt Task Pipeline</description>
|
||||
|
||||
<url type="website">https://github.com/ros-planning/moveit_task_constructor</url>
|
||||
<url type="repository">https://github.com/ros-planning/moveit_task_constructor</url>
|
||||
<url type="bugtracker">https://github.com/ros-planning/moveit_task_constructor/issues</url>
|
||||
|
||||
<license>BSD</license>
|
||||
<maintainer email="me@v4hn.de">Michael Goerner</maintainer>
|
||||
<maintainer email="rhaschke@techfak.uni-bielefeld.de">Robert Haschke</maintainer>
|
||||
|
||||
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend>
|
||||
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake_python</buildtool_depend>
|
||||
|
||||
<depend>geometry_msgs</depend>
|
||||
<depend>moveit_core</depend>
|
||||
@ -21,6 +26,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<test_depend>ament_cmake_gmock</test_depend>
|
||||
<test_depend>ament_cmake_gtest</test_depend>
|
||||
<test_depend>ament_cmake_pytest</test_depend>
|
||||
<test_depend>moveit_configs_utils</test_depend>
|
||||
<!-- TODO(JafarAbdi): Enable after porting integration tests-->
|
||||
<!-- test_depend>launch</test_depend -->
|
||||
|
||||
44
core/python/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
44
core/python/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
# We rely on pybind11's smart_holder branch imported pybind11 via git submodule
|
||||
|
||||
find_package(ament_cmake_python REQUIRED)
|
||||
find_package(Python3 COMPONENTS Interpreter Development)
|
||||
|
||||
# Use minimum-size optimization for pybind11 bindings
|
||||
add_compile_options("-Os")
|
||||
|
||||
# configure pybind11 install for use by downstream packages in install space
|
||||
set(PYBIND11_INSTALL ON CACHE INTERNAL "Install pybind11")
|
||||
set(CMAKE_INSTALL_INCLUDEDIR include/moveit/python)
|
||||
set(PYBIND11_CMAKECONFIG_INSTALL_DIR share/${PROJECT_NAME}/cmake
|
||||
CACHE INTERNAL "install path for pybind11 cmake files")
|
||||
|
||||
# source pybind11 folder, which exposes its targets and installs them
|
||||
if(NOT EXISTS "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/pybind11/CMakeLists.txt")
|
||||
message("Missing content of submodule pybind11: Use 'git clone --recurse-submodule' in future.\n"
|
||||
"Checking out content automatically")
|
||||
execute_process(COMMAND git submodule init
|
||||
COMMAND git submodule update
|
||||
WORKING_DIRECTORY ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR})
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
add_subdirectory(pybind11)
|
||||
|
||||
# C++ wrapper code
|
||||
add_subdirectory(bindings)
|
||||
|
||||
ament_python_install_package("src")
|
||||
|
||||
if(BUILD_TESTING)
|
||||
find_package(ament_cmake_pytest REQUIRED)
|
||||
set(_pytest_tests
|
||||
test/test_mtc.py
|
||||
test/rostest_mtc.py
|
||||
)
|
||||
foreach(_test_path ${_pytest_tests})
|
||||
get_filename_component(_test_name ${_test_path} NAME_WE)
|
||||
ament_add_pytest_test(${_test_name} ${_test_path}
|
||||
APPEND_ENV PYTHONPATH=${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}
|
||||
TIMEOUT 60
|
||||
WORKING_DIRECTORY ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}
|
||||
)
|
||||
endforeach()
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
42
core/python/bindings/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
42
core/python/bindings/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
# python tools support lib
|
||||
set(TOOLS_LIB_NAME moveit_python_tools)
|
||||
set(INCLUDES ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include/moveit/python/python_tools)
|
||||
add_library(${TOOLS_LIB_NAME} SHARED
|
||||
${INCLUDES}/ros_init.h
|
||||
${INCLUDES}/ros_types.h
|
||||
src/ros_init.cpp
|
||||
src/ros_types.cpp
|
||||
)
|
||||
target_include_directories(${TOOLS_LIB_NAME}
|
||||
PUBLIC $<BUILD_INTERFACE:${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>
|
||||
PUBLIC $<INSTALL_INTERFACE:include>
|
||||
)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(${TOOLS_LIB_NAME} PUBLIC pybind11::pybind11 ${Boost_LIBRARIES} rclcpp::rclcpp)
|
||||
|
||||
install(TARGETS ${TOOLS_LIB_NAME}
|
||||
ARCHIVE DESTINATION lib
|
||||
LIBRARY DESTINATION lib
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# moveit.python_tools
|
||||
pybind11_add_module(pymoveit_python_tools src/python_tools.cpp)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(pymoveit_python_tools PRIVATE ${TOOLS_LIB_NAME})
|
||||
|
||||
# moveit.task_constructor
|
||||
set(INCLUDES ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include/moveit/python/task_constructor)
|
||||
pybind11_add_module(pymoveit_mtc
|
||||
${INCLUDES}/properties.h
|
||||
|
||||
src/properties.cpp
|
||||
src/solvers.cpp
|
||||
src/core.cpp
|
||||
src/stages.cpp
|
||||
src/module.cpp
|
||||
)
|
||||
target_include_directories(pymoveit_mtc PUBLIC $<BUILD_INTERFACE:${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(pymoveit_mtc PUBLIC ${PROJECT_NAME} ${PROJECT_NAME}_stages ${TOOLS_LIB_NAME})
|
||||
|
||||
# install python libs
|
||||
install(TARGETS pymoveit_python_tools pymoveit_mtc
|
||||
LIBRARY DESTINATION "${PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR}/${PROJECT_NAME}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
514
core/python/bindings/src/core.cpp
Normal file
514
core/python/bindings/src/core.cpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,514 @@
|
||||
/*********************************************************************
|
||||
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2020, Bielefeld University
|
||||
* All rights reserved.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
|
||||
* are met:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
|
||||
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
|
||||
* with the distribution.
|
||||
* * Neither the name of Bielefeld University nor the names of its
|
||||
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
|
||||
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
|
||||
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
|
||||
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
|
||||
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
|
||||
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
|
||||
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
|
||||
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
*********************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "core.h"
|
||||
#include <pybind11/stl.h>
|
||||
#include <pybind11/functional.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/python/task_constructor/properties.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/container_p.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/task.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <moveit/planning_scene/planning_scene.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/planning_scene_interface/planning_scene_interface.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/move_group_interface/move_group_interface.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace py = pybind11;
|
||||
using namespace py::literals;
|
||||
using namespace moveit::task_constructor;
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace python {
|
||||
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
// utility function to normalize index: negative indeces reference from the end
|
||||
size_t normalize_index(size_t size, long index) {
|
||||
if (index < 0)
|
||||
index += size;
|
||||
if (index >= long(size) || index < 0)
|
||||
throw pybind11::index_error("Index out of range");
|
||||
return index;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// implement operator[](index)
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
typename T::value_type get_item(const T& container, long index) {
|
||||
auto it = container.begin();
|
||||
std::advance(it, normalize_index(container.size(), index));
|
||||
return *it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
py::list getForwardedProperties(const Stage& self) {
|
||||
py::list l;
|
||||
for (const std::string& value : self.forwardedProperties())
|
||||
l.append(value);
|
||||
return l;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void setForwardedProperties(Stage& self, const py::object& names) {
|
||||
std::set<std::string> s;
|
||||
try {
|
||||
// handle string argument as single name
|
||||
if (PyBytes_Check(names.ptr()))
|
||||
s.emplace(names.cast<std::string>());
|
||||
else // expect iterable otherwise
|
||||
for (auto item : names)
|
||||
s.emplace(item.cast<std::string>());
|
||||
} catch (const py::cast_error& e) {
|
||||
// manually translate cast_error to type error
|
||||
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, e.what());
|
||||
throw py::error_already_set();
|
||||
}
|
||||
self.setForwardedProperties(s);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // anonymous namespace
|
||||
|
||||
void export_core(pybind11::module& m) {
|
||||
/// translate InitStageException into InitStageError
|
||||
static py::exception<InitStageException> init_stage_error(m, "InitStageError");
|
||||
/// provide extended error description for InitStageException
|
||||
py::register_exception_translator([](std::exception_ptr p) { // NOLINT(performance-unnecessary-value-param)
|
||||
try {
|
||||
if (p)
|
||||
std::rethrow_exception(p);
|
||||
} catch (const InitStageException& e) {
|
||||
std::stringstream message;
|
||||
message << e;
|
||||
init_stage_error(message.str().c_str());
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<SolutionBase>(m, "Solution", "Abstract base class for solutions of a stage")
|
||||
.def_property("cost", &SolutionBase::cost, &SolutionBase::setCost, "float: Cost associated with the solution")
|
||||
.def_property("comment", &SolutionBase::comment, &SolutionBase::setComment,
|
||||
"str: Comment associated with the solution")
|
||||
.def("markAsFailure", &SolutionBase::markAsFailure, "Mark the SubTrajectory as a failure", "comment"_a)
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("isFailure", &SolutionBase::isFailure,
|
||||
"bool: True if the trajectory is marked as a failure (read-only)")
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("start", &SolutionBase::start, "InterfaceState: Start of the trajectory (read-only)")
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("end", &SolutionBase::end, "InterfaceState: End of the trajectory (read-only)")
|
||||
.def_property_readonly(
|
||||
"markers", py::overload_cast<>(&SolutionBase::markers),
|
||||
":visualization_msgs:`Marker`: Markers to visualize important aspects of the trajectory (read-only)")
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"toMsg",
|
||||
[](const SolutionBasePtr& s) {
|
||||
moveit_task_constructor_msgs::Solution msg;
|
||||
s->fillMessage(msg);
|
||||
return msg;
|
||||
},
|
||||
"Convert to the ROS message ``Solution``");
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<SubTrajectory, SolutionBase>(m, "SubTrajectory",
|
||||
"Solution trajectory connecting two InterfaceStates of a stage")
|
||||
.def(py::init<>())
|
||||
.def_property("trajectory", &SubTrajectory::trajectory, &SubTrajectory::setTrajectory,
|
||||
":moveit_msgs:`RobotTrajectory`: Actual robot trajectory");
|
||||
|
||||
using Solutions = ordered<SolutionBaseConstPtr>;
|
||||
py::classh<Solutions>(m, "Solutions", "Cost-ordered list of solutions")
|
||||
.def("__len__", &Solutions::size)
|
||||
.def("__getitem__", &get_item<Solutions>)
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"__iter__", [](Solutions& self) { return py::make_iterator(self.begin(), self.end()); },
|
||||
py::keep_alive<0, 1>());
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<InterfaceState>(m, "InterfaceState",
|
||||
"Describes a potential start or goal state of a Stage. "
|
||||
"It comprises a PlanningScene as well as a PropertyMap.")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const planning_scene::PlanningScenePtr&>(), "scene"_a)
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("properties", py::overload_cast<>(&InterfaceState::properties),
|
||||
"PropertyMap: PropertyMap of the state (read-only).")
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("scene", &InterfaceState::scene,
|
||||
"PlanningScene: PlanningScene of the state (read-only).");
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode>(m, "MoveItErrorCode", "Encapsulates moveit error code message")
|
||||
.def_readonly("val", &moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode::val, ":moveit_msgs:`MoveItErrorCodes`: error code")
|
||||
.def(PYBIND11_BOOL_ATTR,
|
||||
[](const moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode& err) { return pybind11::cast(static_cast<bool>(err)); });
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<CostTerm>(m, "CostTerm", "Base class for cost calculation in stages");
|
||||
auto tct = py::classh<TrajectoryCostTerm, CostTerm>(m, "TrajectoryCostTerm",
|
||||
"Base class for cost calculation of trajectories");
|
||||
py::enum_<TrajectoryCostTerm::Mode>(tct, "Mode", "Specify which states are considered for collision checking")
|
||||
.value("AUTO", TrajectoryCostTerm::Mode::AUTO, "TRAJECTORY (if available) or START_INTERFACE")
|
||||
.value("START_INTERFACE", TrajectoryCostTerm::Mode::START_INTERFACE, "Only consider start state")
|
||||
.value("END_INTERFACE", TrajectoryCostTerm::Mode::END_INTERFACE, "Only consider end state")
|
||||
.value("TRAJECTORY", TrajectoryCostTerm::Mode::TRAJECTORY, "Consider whole trajectory");
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<cost::PathLength, TrajectoryCostTerm>(m, "PathLength",
|
||||
"Computes joint-based path length along trajectory")
|
||||
.def(py::init<>())
|
||||
.def(py::init<std::vector<std::string>>())
|
||||
.def(py::init<std::map<std::string, double>>());
|
||||
py::classh<cost::DistanceToReference, TrajectoryCostTerm>(m, "DistanceToReference",
|
||||
"Computes joint-based distance to reference pose")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const moveit_msgs::RobotState&, TrajectoryCostTerm::Mode, std::map<std::string, double>>(),
|
||||
"reference"_a, "mode"_a = TrajectoryCostTerm::Mode::AUTO, "weights"_a = std::map<std::string, double>())
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::map<std::string, double>&, TrajectoryCostTerm::Mode, std::map<std::string, double>>(),
|
||||
"reference"_a, "mode"_a = TrajectoryCostTerm::Mode::AUTO, "weights"_a = std::map<std::string, double>());
|
||||
py::classh<cost::TrajectoryDuration, TrajectoryCostTerm>(m, "TrajectoryDuration", "Computes duration of trajectory")
|
||||
.def(py::init<>());
|
||||
py::classh<cost::LinkMotion, TrajectoryCostTerm>(m, "LinkMotion",
|
||||
"Computes Cartesian path length of given link along trajectory")
|
||||
.def(py::init<std::string>(), "link_name"_a);
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<cost::Clearance, TrajectoryCostTerm>(m, "Clearance", "Computes inverse distance to collision objects")
|
||||
.def(py::init<bool, bool, std::string, TrajectoryCostTerm::Mode>(), "with_world"_a = true,
|
||||
"cumulative"_a = false, "group_property"_a = "group", "mode"_a = TrajectoryCostTerm::Mode::AUTO);
|
||||
|
||||
auto stage =
|
||||
properties::class_<Stage, PyStage<>>(m, "Stage", "Abstract base class of all stages.")
|
||||
.property<double>("timeout", "float: Maximally allowed time [s] per computation step")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("marker_ns", "str: Namespace for any markers that are associated to the stage")
|
||||
.def_property("forwarded_properties", getForwardedProperties, setForwardedProperties,
|
||||
"list: set of properties forwarded from input to output InterfaceState")
|
||||
.def_property("name", &Stage::name, &Stage::setName, "str: name of the stage displayed e.g. in rviz")
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("properties", py::overload_cast<>(&Stage::properties),
|
||||
"PropertyMap: PropertyMap of the stage (read-only)")
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("solutions", &Stage::solutions, "Successful Solutions of the stage (read-only)")
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("failures", &Stage::failures, "Solutions: Failed Solutions of the stage (read-only)")
|
||||
.def<void (Stage::*)(const CostTermConstPtr&)>("setCostTerm", &Stage::setCostTerm,
|
||||
"Specify a CostTerm for calculation of stage costs")
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"setCostTerm", [](Stage& self, const LambdaCostTerm::SubTrajectorySignature& f) { self.setCostTerm(f); },
|
||||
"Specify a function to calculate trajectory costs")
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"setCostTerm",
|
||||
[](Stage& self, const LambdaCostTerm::SubTrajectoryShortSignature& f) { self.setCostTerm(f); },
|
||||
"Specify a function to calculate trajectory costs")
|
||||
.def("reset", &Stage::reset, "Reset the Stage. Clears all solutions, interfaces and inherited properties")
|
||||
.def("init", &Stage::init,
|
||||
"Initialize the stage once before planning. "
|
||||
"Will setup properties configured for initialization from parent.",
|
||||
"robot_model"_a);
|
||||
|
||||
py::enum_<Stage::PropertyInitializerSource>(
|
||||
stage, "PropertyInitializerSource",
|
||||
"OR-combinable flags defining a source to initialize a specific property from. "
|
||||
"Used in :doc:`pymoveit_mtc.core.PropertyMap` ``configureInitFrom()``. ")
|
||||
.value("PARENT", Stage::PARENT, "Inherit properties from parent stage")
|
||||
.value("INTERFACE", Stage::INTERFACE, "Inherit properties from the input InterfaceState");
|
||||
|
||||
auto either_way = py::classh<PropagatingEitherWay, Stage, PyPropagatingEitherWay<>>(
|
||||
m, "PropagatingEitherWay", "Base class for propagator-like stages")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("PropagatingEitherWay"))
|
||||
.def("restrictDirection", &PropagatingEitherWay::restrictDirection,
|
||||
"Explicitly specify computation direction")
|
||||
.def("computeForward", &PropagatingEitherWay::computeForward, "Compute forward")
|
||||
.def("computeBackward", &PropagatingEitherWay::computeBackward, "Compute backward")
|
||||
//.def("sendForward", &PropagatingEitherWay::sendForward)
|
||||
//.def("sendBackward", &PropagatingEitherWay::sendBackward)
|
||||
;
|
||||
|
||||
py::enum_<PropagatingEitherWay::Direction>(either_way, "Direction", "Propagation direction")
|
||||
.value("AUTO", PropagatingEitherWay::AUTO)
|
||||
.value("FORWARD", PropagatingEitherWay::FORWARD, "Propagating forwards from start to end")
|
||||
.value("BACKWARD", PropagatingEitherWay::BACKWARD, "Propagating backwards from end to start");
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<PropagatingForward, Stage, PyPropagatingEitherWay<PropagatingForward>>(
|
||||
m, "PropagatingForward", "Base class for forward-propagating stages")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("PropagatingForward"));
|
||||
py::classh<PropagatingBackward, Stage, PyPropagatingEitherWay<PropagatingBackward>>(
|
||||
m, "PropagatingBackward", "Base class for backward-propagating stages")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("PropagatingBackward"));
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<Generator, Stage, PyGenerator<>>(m, "Generator", R"(
|
||||
Base class for generator-like stages
|
||||
|
||||
Derive from this stage to implement a custom generator stage that can produce new seed states w/o prior knowledge.
|
||||
Implement the virtual methods as follows::
|
||||
|
||||
class MyGenerator(core.Generator):
|
||||
"""Implements a custom 'Generator' stage that produces maximally 3 solutions."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, name="Generator"):
|
||||
core.Generator.__init__(self, name)
|
||||
self.reset()
|
||||
|
||||
def init(self, robot_model):
|
||||
self.ps = PlanningScene(robot_model)
|
||||
|
||||
def reset(self):
|
||||
core.Generator.reset(self)
|
||||
|
||||
def canCompute(self):
|
||||
return len(self.solutions) < 3 # maximally produce 3 solutions
|
||||
|
||||
def compute(self):
|
||||
self.spawn(core.InterfaceState(self.ps), cost=len(self.solutions))
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("Generator"))
|
||||
.def("canCompute", &Generator::canCompute, "Return ``True`` if the stage can still produce solutions.")
|
||||
.def("compute", &Generator::compute, "Compute an actual solution and ``spawn`` an ``InterfaceState``")
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"spawn", [](Generator& self, InterfaceState& state, double cost) { self.spawn(std::move(state), cost); },
|
||||
"Spawn an ``InterfaceState`` to both, start and end interface", "state"_a, "cost"_a);
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<MonitoringGenerator, Generator, PyMonitoringGenerator<>>(m, "MonitoringGenerator", R"(
|
||||
Base class for monitoring generator stages
|
||||
|
||||
To implement a generator stage that draws on some previously computed solution, you need to derive
|
||||
from ``MonitoringGenerator`` - monitoring the solutions produced by another stage.
|
||||
Each time, the monitored stage produces a new solution, the method ``onNewSolution()`` of the
|
||||
MonitoringGenerator is called. Usually, you schedule this solution for later processing in ``compute()``::
|
||||
|
||||
class PyMonitoringGenerator(core.MonitoringGenerator):
|
||||
""" Implements a custom 'MonitoringGenerator' stage."""
|
||||
|
||||
solution_multiplier = 2
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, name="MonitoringGenerator"):
|
||||
core.MonitoringGenerator.__init__(self, name)
|
||||
self.reset()
|
||||
|
||||
def reset(self):
|
||||
core.MonitoringGenerator.reset(self)
|
||||
self.pending = []
|
||||
|
||||
def onNewSolution(self, sol):
|
||||
self.pending.append(sol)
|
||||
|
||||
def canCompute(self):
|
||||
return bool(self.pending)
|
||||
|
||||
def compute(self):
|
||||
# fetch first pending upstream solution ...
|
||||
scene = self.pending.pop(0).end.scene
|
||||
# ... and generate new solutions derived from it
|
||||
for i in range(self.solution_multiplier):
|
||||
self.spawn(core.InterfaceState(scene), i)
|
||||
|
||||
Upon creation of the stage, assign the monitored stage as follows::
|
||||
|
||||
jointspace = core.JointInterpolationPlanner()
|
||||
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
current = stages.CurrentState("current")
|
||||
task.add(current)
|
||||
|
||||
connect = stages.Connect(planners=[('panda_arm', jointspace)])
|
||||
task.add(connect)
|
||||
|
||||
mg = PyMonitoringGenerator("generator")
|
||||
mg.setMonitoredStage(task["current"])
|
||||
task.add(mg)
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("generator"))
|
||||
.def("setMonitoredStage", &MonitoringGenerator::setMonitoredStage, "Set the monitored ``Stage``", "stage"_a)
|
||||
.def("_onNewSolution", &PubMonitoringGenerator::onNewSolution);
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<ContainerBase, Stage>(m, "ContainerBase", R"(
|
||||
Abstract base class for container stages
|
||||
Containers allow encapsulation and reuse of planning functionality in a hierachical fashion.
|
||||
You can iterate of the children of a container and access them by name.)")
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"add",
|
||||
[](ContainerBase& c, const py::args& args) {
|
||||
for (auto it = args.begin(), end = args.end(); it != end; ++it)
|
||||
c.add(it->cast<Stage::pointer>());
|
||||
},
|
||||
"Insert a stage at the end of the current children list")
|
||||
.def("insert", &ContainerBase::insert, "stage"_a, "before"_a = -1,
|
||||
"Insert a stage before the given index into the children list")
|
||||
.def("remove", py::overload_cast<int>(&ContainerBase::remove), "Remove child stage by index", "pos"_a)
|
||||
.def("remove", py::overload_cast<Stage*>(&ContainerBase::remove), "Remove child stage by instance", "child"_a)
|
||||
.def("clear", &ContainerBase::clear, "Remove all stages from the container")
|
||||
.def("__len__", &ContainerBase::numChildren)
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"__getitem__",
|
||||
[](const ContainerBase& c, const std::string& name) -> Stage* {
|
||||
Stage* child = c.findChild(name);
|
||||
if (!child)
|
||||
throw py::index_error();
|
||||
return child;
|
||||
},
|
||||
py::return_value_policy::reference_internal)
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"__getitem__",
|
||||
[](const ContainerBase& c, int idx) -> Stage* {
|
||||
Stage* child = c[idx];
|
||||
if (!child)
|
||||
throw py::index_error();
|
||||
return child;
|
||||
},
|
||||
py::return_value_policy::reference_internal)
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"__iter__",
|
||||
[](const ContainerBase& c) {
|
||||
const auto& children = c.pimpl()->children();
|
||||
return py::make_iterator(children.begin(), children.end());
|
||||
},
|
||||
py::keep_alive<0, 1>()) // keep container alive as long as iterator lives
|
||||
;
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<SerialContainer, ContainerBase>(m, "SerialContainer", "Container implementing a linear planning sequence")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("SerialContainer"));
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<ParallelContainerBase, ContainerBase>(m, "ParallelContainerBase",
|
||||
"Abstract base class for parallel containers");
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<Alternatives, ParallelContainerBase>(m, "Alternatives", R"(
|
||||
Plan for different alternatives in parallel.
|
||||
Solutions of all children are considered simultaneously.
|
||||
See :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-alternatives>` for an example.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("Alternatives"));
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<Fallbacks, ParallelContainerBase>(m, "Fallbacks", R"(
|
||||
Plan for different alternatives in sequence
|
||||
Try to find feasible solutions using the children in sequence. The behaviour slightly differs for the indivual stage types:
|
||||
|
||||
- Generator: Proceed to next child if currently active one exhausted its solution, i.e. returns ``canCompute() == False``.
|
||||
- Propagator: Forward an incoming ``InterfaceState`` to the next child if the current one ultimately failed on it.
|
||||
- Connect: Only ``Connect`` stages are supported. Pairs of ``InterfaceStates`` are forward to the next child on failure of the current child.
|
||||
|
||||
See :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-fallbacks>` for an example.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("Fallbacks"));
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<Merger, ParallelContainerBase>(m, "Merger", R"(
|
||||
Plan for different sub tasks in parallel and eventually merge all sub solutions into a single trajectory
|
||||
This requires all children to operate on disjoint ``JointModelGroups``.
|
||||
|
||||
See :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-merger>` for an example.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("merger"));
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<WrapperBase, ParallelContainerBase>(m, "WrapperBase", R"(
|
||||
Base class for wrapping containers, which can be used to filter or modify solutions generated by the single child.
|
||||
Implementations of this interface need to implement ``onNewSolution()`` to process a solution generated by the child.
|
||||
The wrapper may reject the solution or create one or multiple derived solutions, potentially adapting the cost,
|
||||
the trajectory and output ``InterfaceStates``.
|
||||
)");
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<Task>(m, "Task", R"(Root stage of a planning pipeline.
|
||||
A task stage usually wraps a single container (by default ``SerialContainer``) stage.
|
||||
The class provides methods to ``plan()`` for the configured pipeline and retrieve full solutions.)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&, bool>(), "ns"_a = std::string(), "introspection"_a = true)
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&, bool, ContainerBase::pointer&&>(), "ns"_a = std::string(),
|
||||
"introspection"_a = true, "container"_a)
|
||||
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("properties", py::overload_cast<>(&Task::properties),
|
||||
"PropertyMap: PropertyMap of the stage (read-only)")
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("solutions", &Task::solutions, "Successful Solutions of the stage (read-only)")
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("failures", &Task::failures, "Solutions: Failed Solutions of the stage (read-only)")
|
||||
.def_property("name", &Task::name, &Task::setName, "str: name of the task displayed e.g. in rviz")
|
||||
|
||||
.def("loadRobotModel", &Task::loadRobotModel, "robot_description"_a = "robot_description",
|
||||
"Load robot model from given ROS parameter")
|
||||
.def("getRobotModel", &Task::getRobotModel)
|
||||
.def("enableIntrospection", &Task::enableIntrospection, "enabled"_a = true,
|
||||
"Enable publishing intermediate results for inspection in ``rviz``")
|
||||
.def("clear", &Task::clear, "Reset the stage task (and all its stages)")
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"add",
|
||||
[](Task& t, const py::args& args) {
|
||||
for (auto it = args.begin(), end = args.end(); it != end; ++it)
|
||||
t.add(it->cast<Stage::pointer>());
|
||||
},
|
||||
"Append stage(s) to the task's top-level container")
|
||||
.def("__len__", [](const Task& t) { t.stages()->numChildren(); })
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"__getitem__",
|
||||
[](const Task& t, const std::string& name) -> Stage* {
|
||||
Stage* child = t.stages()->findChild(name);
|
||||
if (!child)
|
||||
throw py::index_error();
|
||||
return child;
|
||||
},
|
||||
py::return_value_policy::reference_internal)
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"__getitem__",
|
||||
[](const Task& t, int idx) -> Stage* {
|
||||
Stage* child = t.stages()->operator[](idx);
|
||||
if (!child)
|
||||
throw py::index_error();
|
||||
return child;
|
||||
},
|
||||
py::return_value_policy::reference_internal)
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"__iter__",
|
||||
[](const Task& t) {
|
||||
const auto& children = t.stages()->pimpl()->children();
|
||||
return py::make_iterator(children.begin(), children.end());
|
||||
},
|
||||
py::keep_alive<0, 1>()) // keep container alive as long as iterator lives
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"setCostTerm", [](Task& self, const CostTermConstPtr& c) { self.setCostTerm(c); },
|
||||
"Specify a CostTerm for calculation of stage costs")
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"setCostTerm", [](Task& self, const LambdaCostTerm::SubTrajectorySignature& f) { self.setCostTerm(f); },
|
||||
"Specify a function to calculate trajectory costs")
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"setCostTerm", [](Task& self, const LambdaCostTerm::SubTrajectoryShortSignature& f) { self.setCostTerm(f); },
|
||||
"Specify a function to calculate trajectory costs")
|
||||
.def("reset", &Task::reset, "Reset task (and all its stages)")
|
||||
.def("init", py::overload_cast<>(&Task::init), "Initialize the task (and all its stages)")
|
||||
.def("plan", &Task::plan, "max_solutions"_a = 0, R"(
|
||||
Reset, init, and plan. Planning is limited to ``max_allowed_solutions``.
|
||||
Returns if planning was successful.)")
|
||||
.def("preempt", &Task::preempt, "Interrupt current planning (or execution)")
|
||||
.def(
|
||||
"publish",
|
||||
[](Task& self, const SolutionBasePtr& solution) { self.introspection().publishSolution(*solution); },
|
||||
"solution"_a, "Publish the given solution to the ROS topic ``solution``")
|
||||
.def_static(
|
||||
"execute",
|
||||
[](const SolutionBasePtr& solution) {
|
||||
using namespace moveit::planning_interface;
|
||||
PlanningSceneInterface psi;
|
||||
MoveGroupInterface mgi(solution->start()->scene()->getRobotModel()->getJointModelGroupNames()[0]);
|
||||
|
||||
MoveGroupInterface::Plan plan;
|
||||
moveit_task_constructor_msgs::Solution serialized;
|
||||
solution->fillMessage(serialized);
|
||||
|
||||
for (const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::SubTrajectory& traj : serialized.sub_trajectory) {
|
||||
if (!traj.trajectory.joint_trajectory.points.empty()) {
|
||||
plan.trajectory_ = traj.trajectory;
|
||||
if (!mgi.execute(plan)) {
|
||||
ROS_ERROR("Execution failed! Aborting!");
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
psi.applyPlanningScene(traj.scene_diff);
|
||||
}
|
||||
ROS_INFO("Executed successfully");
|
||||
},
|
||||
"solution"_a, "Send given solution to ``move_group`` node for execution");
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace python
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
145
core/python/bindings/src/core.h
Normal file
145
core/python/bindings/src/core.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
|
||||
/*********************************************************************
|
||||
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2020, Bielefeld University
|
||||
* All rights reserved.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
|
||||
* are met:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
|
||||
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
|
||||
* with the distribution.
|
||||
* * Neither the name of Bielefeld University nor the names of its
|
||||
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
|
||||
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
|
||||
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
|
||||
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
|
||||
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
|
||||
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
|
||||
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
|
||||
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
*********************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#pragma once
|
||||
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/stage.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/container.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/cost_queue.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/cost_terms.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/utils/moveit_error_code.h>
|
||||
#include <pybind11/smart_holder.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/** Trampoline classes to allow inheritance in Python (overriding virtual functions) */
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace task_constructor {
|
||||
|
||||
class Task;
|
||||
namespace solvers {
|
||||
class PlannerInterface;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <class Stage = moveit::task_constructor::Stage>
|
||||
class PyStage : public Stage, public pybind11::trampoline_self_life_support
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using Stage::Stage;
|
||||
|
||||
void init(const moveit::core::RobotModelConstPtr& robot_model) override {
|
||||
PYBIND11_OVERRIDE(void, Stage, init, robot_model);
|
||||
}
|
||||
void reset() override { PYBIND11_OVERRIDE(void, Stage, reset, ); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <class Generator = moveit::task_constructor::Generator>
|
||||
class PyGenerator : public PyStage<Generator>
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using PyStage<Generator>::PyStage;
|
||||
bool canCompute() const override { PYBIND11_OVERRIDE_PURE(bool, Generator, canCompute, ); }
|
||||
void compute() override { PYBIND11_OVERRIDE_PURE(void, Generator, compute, ); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <class MonitoringGenerator = moveit::task_constructor::MonitoringGenerator>
|
||||
class PyMonitoringGenerator : public PyGenerator<MonitoringGenerator>
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using PyGenerator<MonitoringGenerator>::PyGenerator;
|
||||
void onNewSolution(const SolutionBase& s) override {
|
||||
// pass solution as pointer to trigger passing by reference
|
||||
PYBIND11_OVERRIDE_PURE(void, MonitoringGenerator, onNewSolution, &s);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Helper class to expose protected member function onNewSolution
|
||||
// https://pybind11.readthedocs.io/en/stable/advanced/classes.html#binding-protected-member-functions
|
||||
class PubMonitoringGenerator : public MonitoringGenerator
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using MonitoringGenerator::onNewSolution;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <class PropagatingEitherWay = moveit::task_constructor::PropagatingEitherWay>
|
||||
class PyPropagatingEitherWay : public PyStage<PropagatingEitherWay>
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using PyStage<PropagatingEitherWay>::PyStage;
|
||||
void computeForward(const InterfaceState& from_state) override {
|
||||
// pass InterfaceState as pointer to trigger passing by reference
|
||||
PYBIND11_OVERRIDE_PURE(void, PropagatingEitherWay, computeForward, &from_state);
|
||||
}
|
||||
void computeBackward(const InterfaceState& to_state) override {
|
||||
// pass InterfaceState as pointer to trigger passing by reference
|
||||
PYBIND11_OVERRIDE_PURE(void, PropagatingEitherWay, computeBackward, &to_state);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace task_constructor
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::Property)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::PropertyMap)
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::solvers::PlannerInterface)
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::SolutionBase)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::SubTrajectory)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(ordered<moveit::task_constructor::SolutionBaseConstPtr>)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::InterfaceState)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode)
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::CostTerm)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::TrajectoryCostTerm)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::cost::PathLength)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::cost::DistanceToReference)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::cost::TrajectoryDuration)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::cost::LinkMotion)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::cost::Clearance)
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::Stage)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::PropagatingEitherWay)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::PropagatingForward)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::PropagatingBackward)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::Generator)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::MonitoringGenerator)
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::ContainerBase)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::SerialContainer)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::ParallelContainerBase)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::Alternatives)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::Fallbacks)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::Merger)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::WrapperBase)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::Task)
|
||||
59
core/python/bindings/src/module.cpp
Normal file
59
core/python/bindings/src/module.cpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
/*********************************************************************
|
||||
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2020, Bielefeld University
|
||||
* All rights reserved.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
|
||||
* are met:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
|
||||
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
|
||||
* with the distribution.
|
||||
* * Neither the name of Bielefeld University nor the names of its
|
||||
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
|
||||
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
|
||||
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
|
||||
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
|
||||
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
|
||||
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
|
||||
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
|
||||
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
*********************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <pybind11/smart_holder.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace python {
|
||||
|
||||
void export_properties(pybind11::module& m);
|
||||
void export_solvers(pybind11::module& m);
|
||||
void export_core(pybind11::module& m);
|
||||
void export_stages(pybind11::module& m);
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace python
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_MODULE(pymoveit_mtc, m) {
|
||||
auto msub = m.def_submodule("core", "Provides wrappers for core C++ classes. "
|
||||
"**Import as** :doc:`moveit.task_constructor.core`.");
|
||||
|
||||
moveit::python::export_properties(msub);
|
||||
moveit::python::export_solvers(msub);
|
||||
moveit::python::export_core(msub);
|
||||
|
||||
msub = m.def_submodule("stages", "Provides wrappers of standard MTC stages. "
|
||||
"**Import as** :doc:`moveit.task_constructor.stages`.");
|
||||
moveit::python::export_stages(msub);
|
||||
}
|
||||
242
core/python/bindings/src/properties.cpp
Normal file
242
core/python/bindings/src/properties.cpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,242 @@
|
||||
/*********************************************************************
|
||||
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2020, Bielefeld University
|
||||
* All rights reserved.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
|
||||
* are met:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
|
||||
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
|
||||
* with the distribution.
|
||||
* * Neither the name of Bielefeld University nor the names of its
|
||||
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
|
||||
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
|
||||
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
|
||||
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
|
||||
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
|
||||
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
|
||||
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
|
||||
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
*********************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <moveit/python/task_constructor/properties.h>
|
||||
#include <boost/core/demangle.hpp>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace py = pybind11;
|
||||
using namespace py::literals;
|
||||
using namespace moveit::task_constructor;
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::Property)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(moveit::task_constructor::PropertyMap)
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace python {
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
class PropertyConverterRegistry
|
||||
{
|
||||
struct Entry
|
||||
{
|
||||
PropertyConverterBase::to_python_converter_function to_;
|
||||
PropertyConverterBase::from_python_converter_function from_;
|
||||
};
|
||||
// map from type_index to corresponding converter functions
|
||||
typedef std::map<std::type_index, Entry> RegistryMap;
|
||||
RegistryMap types_;
|
||||
// map from ros-msg-names to entry in types_
|
||||
using RosMsgTypeNameMap = std::map<std::string, RegistryMap::iterator>;
|
||||
RosMsgTypeNameMap msg_names_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
PropertyConverterRegistry();
|
||||
|
||||
inline bool insert(const std::type_index& type_index, const std::string& ros_msg_name,
|
||||
PropertyConverterBase::to_python_converter_function to,
|
||||
PropertyConverterBase::from_python_converter_function from);
|
||||
|
||||
static py::object toPython(const boost::any& value);
|
||||
|
||||
static boost::any fromPython(const py::object& bpo);
|
||||
};
|
||||
static PropertyConverterRegistry REGISTRY_SINGLETON;
|
||||
|
||||
PropertyConverterRegistry::PropertyConverterRegistry() {
|
||||
// register property converters
|
||||
PropertyConverter<bool>();
|
||||
PropertyConverter<int>();
|
||||
PropertyConverter<unsigned int>();
|
||||
PropertyConverter<long>();
|
||||
PropertyConverter<float>();
|
||||
PropertyConverter<double>();
|
||||
PropertyConverter<std::string>();
|
||||
PropertyConverter<std::set<std::string>>();
|
||||
PropertyConverter<std::map<std::string, double>>();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool PropertyConverterRegistry::insert(const std::type_index& type_index, const std::string& ros_msg_name,
|
||||
PropertyConverterBase::to_python_converter_function to,
|
||||
PropertyConverterBase::from_python_converter_function from) {
|
||||
auto it_inserted = types_.insert(std::make_pair(type_index, Entry{ to, from }));
|
||||
if (!it_inserted.second)
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!ros_msg_name.empty()) // is this a ROS msg type?
|
||||
msg_names_.insert(std::make_pair(ros_msg_name, it_inserted.first));
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
py::object PropertyConverterRegistry::toPython(const boost::any& value) {
|
||||
if (value.empty())
|
||||
return py::object();
|
||||
|
||||
auto it = REGISTRY_SINGLETON.types_.find(value.type());
|
||||
if (it == REGISTRY_SINGLETON.types_.end()) {
|
||||
std::string msg("No Python -> C++ conversion for: ");
|
||||
msg += boost::core::demangle(value.type().name());
|
||||
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, msg.c_str());
|
||||
throw py::error_already_set();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return it->second.to_(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::string rosMsgName(PyObject* object) {
|
||||
py::object o = py::reinterpret_borrow<py::object>(object);
|
||||
try {
|
||||
return o.attr("_type").cast<std::string>();
|
||||
} catch (const py::error_already_set&) {
|
||||
// change error to TypeError
|
||||
std::string msg = o.attr("__class__").attr("__name__").cast<std::string>();
|
||||
msg += " is not a ROS message type";
|
||||
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, msg.c_str());
|
||||
throw py::error_already_set();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
boost::any PropertyConverterRegistry::fromPython(const py::object& po) {
|
||||
PyObject* o = po.ptr();
|
||||
|
||||
if (PyBool_Check(o))
|
||||
return (o == Py_True);
|
||||
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
|
||||
if (PyLong_Check(o))
|
||||
return PyLong_AS_LONG(o);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
if (PyInt_Check(o))
|
||||
return PyInt_AS_LONG(o);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
if (PyFloat_Check(o))
|
||||
return PyFloat_AS_DOUBLE(o);
|
||||
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
|
||||
if (PyUnicode_Check(o))
|
||||
#else
|
||||
if (PyString_Check(o))
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return py::cast<std::string>(o);
|
||||
|
||||
const std::string& ros_msg_name = rosMsgName(o);
|
||||
auto it = REGISTRY_SINGLETON.msg_names_.find(ros_msg_name);
|
||||
if (it == REGISTRY_SINGLETON.msg_names_.end()) {
|
||||
std::string msg("No Python -> C++ conversion for: ");
|
||||
msg += ros_msg_name;
|
||||
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, msg.c_str());
|
||||
throw py::error_already_set();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return it->second->second.from_(po);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // end anonymous namespace
|
||||
|
||||
bool PropertyConverterBase::insert(const std::type_index& type_index, const std::string& ros_msg_name,
|
||||
moveit::python::PropertyConverterBase::to_python_converter_function to,
|
||||
moveit::python::PropertyConverterBase::from_python_converter_function from) {
|
||||
return REGISTRY_SINGLETON.insert(type_index, ros_msg_name, to, from);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void export_properties(py::module& m) {
|
||||
// clang-format off
|
||||
py::classh<Property>(m, "Property", "Holds an arbitrarily typed value and a default value")
|
||||
.def(py::init<>())
|
||||
.def("setValue", [](Property& self, const py::object& value)
|
||||
{ self.setValue(PropertyConverterRegistry::fromPython(value)); },
|
||||
"Set current and default value.", "value"_a)
|
||||
.def("setCurrentValue", [](Property& self, const py::object& value)
|
||||
{ self.setCurrentValue(PropertyConverterRegistry::fromPython(value)); },
|
||||
"Set the current value only, w/o touching the default.", "value"_a)
|
||||
.def("value", [](const Property& self)
|
||||
{ return PropertyConverterRegistry::toPython(self.value()); }, "Retrieve the stored value.")
|
||||
.def("defaultValue", [](const Property& self)
|
||||
{ return PropertyConverterRegistry::toPython(self.defaultValue()); },
|
||||
"Retrieve the default value.")
|
||||
.def("reset", &Property::reset, "Reset the value to the stored default.")
|
||||
.def("defined", &Property::defined, "Was a (non-default) value stored?")
|
||||
.def("description", &Property::description, "Retrive the property description string")
|
||||
.def("setDescription", &Property::setDescription,
|
||||
"Set the property's description", "desc"_a);
|
||||
|
||||
py::classh<PropertyMap>(m, "PropertyMap", "Dictionary of named :doc:`properties <pymoveit_mtc.core.Property>`")
|
||||
.def(py::init<>())
|
||||
.def("__bool__", [](const PropertyMap& self) { return self.begin() == self.end();})
|
||||
.def("__iter__", [](PropertyMap& self) { return py::make_key_iterator(self.begin(), self.end()); },
|
||||
py::keep_alive<0, 1>()) // Essential: keep list alive while iterator exists
|
||||
.def("items", [](const PropertyMap& self) { return py::make_iterator(self.begin(), self.end()); },
|
||||
py::keep_alive<0, 1>(), "Retrieve an iterator over the items of the dictionary.")
|
||||
.def("__contains__", [](const PropertyMap& self, const std::string &key) { return self.hasProperty(key); })
|
||||
.def("property", [](PropertyMap& self, const std::string& key)
|
||||
{ return self.property(key); }, py::return_value_policy::reference_internal, R"(
|
||||
Retrieve the property instance for the given key.
|
||||
This is in contrast to ``map[key]``, which returns ``map.property(key).value()``.)",
|
||||
"key"_a)
|
||||
.def("__getitem__", [](const PropertyMap& self, const std::string& key)
|
||||
{ return PropertyConverterRegistry::toPython(self.get(key)); })
|
||||
.def("__setitem__", [](PropertyMap& self, const std::string& key, const py::object& value)
|
||||
{ self.set(key, PropertyConverterRegistry::fromPython(value)); })
|
||||
.def("reset", &PropertyMap::reset, "Reset all properties to their default values")
|
||||
.def("update", [](PropertyMap& self, const py::dict& values) {
|
||||
for (auto it = values.begin(), end = values.end(); it != end; ++it) {
|
||||
self.set(it->first.cast<std::string>(),
|
||||
PropertyConverterRegistry::fromPython(py::reinterpret_borrow<py::object>(it->second)));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, "Update property values from another dictionary", "values"_a)
|
||||
.def("configureInitFrom", [](PropertyMap& self, Property::SourceFlags sources, const py::list& names) {
|
||||
std::set<std::string> s;
|
||||
for (auto& item : names)
|
||||
s.insert(item.cast<std::string>());
|
||||
self.configureInitFrom(sources, s);
|
||||
}, "Configure initialization of listed (or all) properties from given source(s).",
|
||||
"sources"_a, "names"_a = py::list())
|
||||
.def("exposeTo", [](PropertyMap& self, PropertyMap& other, const std::string& name) {
|
||||
self.exposeTo(other, name, name);
|
||||
}, "Declare ``named`` property in ``other`` PropertyMap - using same name.",
|
||||
"other"_a, "name"_a)
|
||||
.def("exposeTo", [](PropertyMap& self, PropertyMap& other, const std::string& name, const std::string& other_name) {
|
||||
self.exposeTo(other, name, other_name);
|
||||
}, "Declare ``named`` property in ``other`` PropertyMap - using ``other_name``.",
|
||||
"other"_a, "name"_a, "other_name"_a)
|
||||
.def("exposeTo", [](PropertyMap& self, PropertyMap& other, const py::list& names) {
|
||||
std::set<std::string> s;
|
||||
for (auto& item : names)
|
||||
s.insert(item.cast<std::string>());
|
||||
self.exposeTo(other, s);
|
||||
}, "Declare `all` ``named`` properties in ``other`` PropertyMap - using the same names.",
|
||||
"other"_a, "names"_a)
|
||||
;
|
||||
// clang-format on
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace python
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
53
core/python/bindings/src/python_tools.cpp
Normal file
53
core/python/bindings/src/python_tools.cpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
/*********************************************************************
|
||||
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2020, Bielefeld University
|
||||
* All rights reserved.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
|
||||
* are met:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
|
||||
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
|
||||
* with the distribution.
|
||||
* * Neither the name of Bielefeld University nor the names of its
|
||||
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
|
||||
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
|
||||
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
|
||||
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
|
||||
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
|
||||
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
|
||||
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
|
||||
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
*********************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <pybind11/smart_holder.h>
|
||||
#include <pybind11/stl.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/python/python_tools/ros_init.h>
|
||||
#include <ros/init.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace py = pybind11;
|
||||
using namespace moveit::python;
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_MODULE(pymoveit_python_tools, m) {
|
||||
m.doc() = "MoveIt python tools";
|
||||
|
||||
m.def("roscpp_init", &InitProxy::init, "Initialize C++ ROS", py::arg("node_name") = "moveit_python_wrapper",
|
||||
py::arg("remappings") = std::map<std::string, std::string>(), py::arg("options") = 0);
|
||||
m.def("roscpp_shutdown", &InitProxy::shutdown, "Shutdown C++ ROS");
|
||||
|
||||
py::enum_<ros::InitOption>(m, "InitOption")
|
||||
.value("AnonymousName", ros::init_options::AnonymousName)
|
||||
.value("NoRosout", ros::init_options::NoRosout);
|
||||
}
|
||||
68
core/python/bindings/src/ros_init.cpp
Normal file
68
core/python/bindings/src/ros_init.cpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
/*********************************************************************
|
||||
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2020, Bielefeld University
|
||||
* All rights reserved.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
|
||||
* are met:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
|
||||
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
|
||||
* with the distribution.
|
||||
* * Neither the name of Bielefeld University nor the names of its
|
||||
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
|
||||
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
|
||||
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
|
||||
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
|
||||
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
|
||||
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
|
||||
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
|
||||
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
*********************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <moveit/python/python_tools/ros_init.h>
|
||||
#include <ros/init.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace python {
|
||||
|
||||
boost::mutex InitProxy::lock_;
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<InitProxy> InitProxy::singleton_instance_;
|
||||
|
||||
void InitProxy::init(const std::string& node_name, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& remappings,
|
||||
uint32_t options) {
|
||||
boost::mutex::scoped_lock slock(lock_);
|
||||
if (!singleton_instance_ && !ros::isInitialized())
|
||||
singleton_instance_.reset(new InitProxy(node_name, remappings, options));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void InitProxy::shutdown() {
|
||||
boost::mutex::scoped_lock slock(lock_);
|
||||
singleton_instance_.reset();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
InitProxy::InitProxy(const std::string& node_name, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& remappings,
|
||||
uint32_t options) {
|
||||
ros::init(remappings, node_name, options | ros::init_options::NoSigintHandler);
|
||||
spinner.reset(new ros::AsyncSpinner(1));
|
||||
spinner->start();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
InitProxy::~InitProxy() {
|
||||
spinner->stop();
|
||||
spinner.reset();
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace python
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
61
core/python/bindings/src/ros_types.cpp
Normal file
61
core/python/bindings/src/ros_types.cpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
/*********************************************************************
|
||||
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2020, Bielefeld University
|
||||
* All rights reserved.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
|
||||
* are met:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
|
||||
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
|
||||
* with the distribution.
|
||||
* * Neither the name of Bielefeld University nor the names of its
|
||||
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
|
||||
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
|
||||
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
|
||||
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
|
||||
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
|
||||
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
|
||||
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
|
||||
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
*********************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <moveit/python/python_tools/ros_types.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace py = pybind11;
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace python {
|
||||
|
||||
py::object createMessage(const std::string& ros_msg_name) {
|
||||
// find delimiting '/' in ros msg name
|
||||
std::size_t pos = ros_msg_name.find('/');
|
||||
// import module
|
||||
py::module m = py::module::import((ros_msg_name.substr(0, pos) + ".msg").c_str());
|
||||
// retrieve type instance
|
||||
py::object cls = m.attr(ros_msg_name.substr(pos + 1).c_str());
|
||||
// create message instance
|
||||
return cls();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool convertible(const pybind11::handle& h, const char* ros_msg_name) {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
PyObject* o = h.attr("_type").ptr();
|
||||
return py::cast<std::string>(o) == ros_msg_name;
|
||||
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace python
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
120
core/python/bindings/src/solvers.cpp
Normal file
120
core/python/bindings/src/solvers.cpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
/*********************************************************************
|
||||
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2020, Bielefeld University
|
||||
* All rights reserved.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
|
||||
* are met:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
|
||||
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
|
||||
* with the distribution.
|
||||
* * Neither the name of Bielefeld University nor the names of its
|
||||
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
|
||||
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
|
||||
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
|
||||
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
|
||||
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
|
||||
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
|
||||
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
|
||||
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
*********************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <moveit/python/task_constructor/properties.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/solvers/cartesian_path.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/solvers/pipeline_planner.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/solvers/joint_interpolation.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit_msgs/WorkspaceParameters.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace py = pybind11;
|
||||
using namespace moveit::task_constructor;
|
||||
using namespace moveit::task_constructor::solvers;
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(PlannerInterface)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(PipelinePlanner)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(JointInterpolationPlanner)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(CartesianPath)
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace python {
|
||||
|
||||
void export_solvers(py::module& m) {
|
||||
properties::class_<PlannerInterface>(m, "PlannerInterface", "Abstract base class for planning algorithms")
|
||||
.property<double>("max_velocity_scaling_factor", "float: Reduce the maximum velocity by scaling between (0,1]")
|
||||
.property<double>("max_acceleration_scaling_factor",
|
||||
"float: Reduce the maximum acceleration by scaling between (0,1]")
|
||||
.def_property_readonly("properties", py::overload_cast<>(&PlannerInterface::properties),
|
||||
py::return_value_policy::reference_internal, "Properties of the planner");
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<PipelinePlanner, PlannerInterface>(m, "PipelinePlanner",
|
||||
R"(Plan using MoveIt's ``PlanningPipeline``
|
||||
::
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core
|
||||
|
||||
# Create and configure a planner instance
|
||||
pipelinePlanner = core.PipelinePlanner()
|
||||
pipelinePlanner.planner = 'PRMkConfigDefault'
|
||||
pipelinePlanner.num_planning_attempts = 10
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("planner", "str: Planner ID")
|
||||
.property<uint>("num_planning_attempts", "int: Number of planning attempts")
|
||||
.property<moveit_msgs::WorkspaceParameters>(
|
||||
"workspace_parameters",
|
||||
":moveit_msgs:`WorkspaceParameters`: Specifies workspace box to be used for Cartesian sampling")
|
||||
.property<double>("goal_joint_tolerance", "float: Tolerance for reaching joint goals")
|
||||
.property<double>("goal_position_tolerance", "float: Tolerance for reaching position goals")
|
||||
.property<double>("goal_orientation_tolerance", "float: Tolerance for reaching orientation goals")
|
||||
.property<bool>("display_motion_plans", "bool: Publish generated solutions via a topic")
|
||||
.property<bool>("publish_planning_requests", "bool: Publish motion planning requests via a topic")
|
||||
.def(py::init<>());
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<JointInterpolationPlanner, PlannerInterface>(
|
||||
m, "JointInterpolationPlanner",
|
||||
R"(Perform linear interpolation between joint space poses.
|
||||
Fails on collision along the interpolation path. There is no obstacle avoidance. ::
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core
|
||||
|
||||
# Instantiate joint-space interpolation planner
|
||||
jointPlanner = core.JointInterpolationPlanner()
|
||||
jointPlanner.max_step = 0.1
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<double>("max_step", "float: Limit any (single) joint change between two waypoints to this amount")
|
||||
.def(py::init<>());
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<CartesianPath, PlannerInterface>(m, "CartesianPath", R"(
|
||||
Perform linear interpolation between Cartesian poses.
|
||||
Fails on collision along the interpolation path. There is no obstacle avoidance. ::
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core
|
||||
|
||||
# Instantiate Cartesian-space interpolation planner
|
||||
cartesianPlanner = core.CartesianPath()
|
||||
cartesianPlanner.step_size = 0.01
|
||||
cartesianPlanner.jump_threshold = 0.0 # effectively disable jump threshold.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<double>("step_size", "float: Limit the Cartesian displacement between consecutive waypoints "
|
||||
"In contrast to joint-space interpolation, the Cartesian planner can also "
|
||||
"succeed when only a fraction of the linear path was feasible.")
|
||||
.property<double>(
|
||||
"jump_threshold",
|
||||
"float: Limit joint displacement between consecutive waypoints, thus preventing jumps in joint space. "
|
||||
"This values specifies the fraction of mean acceptable joint motion per step.")
|
||||
.property<double>("min_fraction", "float: Fraction of overall distance required to succeed.")
|
||||
.def(py::init<>());
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace python
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
531
core/python/bindings/src/stages.cpp
Normal file
531
core/python/bindings/src/stages.cpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,531 @@
|
||||
/*********************************************************************
|
||||
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2020, Bielefeld University
|
||||
* All rights reserved.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
|
||||
* are met:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
|
||||
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
|
||||
* with the distribution.
|
||||
* * Neither the name of Bielefeld University nor the names of its
|
||||
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
|
||||
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
|
||||
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
|
||||
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
|
||||
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
|
||||
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
|
||||
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
|
||||
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
*********************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "stages.h"
|
||||
#include <moveit/python/task_constructor/properties.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/stages.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/stages/pick.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/stages/simple_grasp.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/planning_scene/planning_scene.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit_msgs/PlanningScene.h>
|
||||
#include <pybind11/stl.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace py = pybind11;
|
||||
using namespace py::literals;
|
||||
using namespace moveit::task_constructor;
|
||||
using namespace moveit::task_constructor::stages;
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(ModifyPlanningScene)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(CurrentState)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(FixedState)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(ComputeIK)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(MoveTo)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(MoveRelative)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(Connect)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(FixCollisionObjects)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(GenerateGraspPose)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(GeneratePlacePose)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(GeneratePose)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(Pick)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(Place)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(SimpleGraspBase)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(SimpleGrasp)
|
||||
PYBIND11_SMART_HOLDER_TYPE_CASTERS(SimpleUnGrasp)
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace python {
|
||||
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
/// extract from python argument a vector<T>, where arg maybe a single T or a list of Ts
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
std::vector<T> elementOrList(const py::object& arg) {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
return std::vector<T>{ arg.cast<T>() };
|
||||
} catch (const py::cast_error&) {
|
||||
return arg.cast<std::vector<T>>();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // anonymous namespace
|
||||
|
||||
void export_stages(pybind11::module& m) {
|
||||
// clang-format off
|
||||
properties::class_<ModifyPlanningScene, Stage>(m, "ModifyPlanningScene", R"(
|
||||
Apply modifications to the PlanningScene w/o moving the robot
|
||||
|
||||
This stage takes the incoming planning scene and applies previously scheduled changes to it, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
* Modify allowed collision matrix, enabling or disabling collision pairs
|
||||
* Attach or detach objects to robot links
|
||||
* Add or remove objects
|
||||
|
||||
For an example, see :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-modify-planning-scene>`.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("modify planning scene"))
|
||||
.def("attachObject", &ModifyPlanningScene::attachObject, "Attach an object to a robot link", "name"_a, "link"_a)
|
||||
.def("detachObject", &ModifyPlanningScene::detachObject, "Detach an object from a robot link", "name"_a, "link"_a)
|
||||
.def("attachObjects", [](ModifyPlanningScene& self, const py::object& names,
|
||||
const std::string& attach_link, bool attach) {
|
||||
self.attachObjects(elementOrList<std::string>(names), attach_link, attach);
|
||||
}, "Attach multiple objects to a robot link", "names"_a, "attach_link"_a, "attach"_a = true)
|
||||
.def("detachObjects", [](ModifyPlanningScene& self, const py::object& names,
|
||||
const std::string& attach_link) {
|
||||
self.attachObjects(elementOrList<std::string>(names), attach_link, false);
|
||||
}, "Detach multiple objects from a robot link", "names"_a, "attach_link"_a)
|
||||
.def("allowCollisions", [](ModifyPlanningScene& self,
|
||||
const py::object& first, const py::object& second, bool enable_collision) {
|
||||
self.allowCollisions(elementOrList<std::string>(first), elementOrList<std::string>(second), enable_collision);
|
||||
}, "Allow or disable collisions between links and objects", "first"_a, "second"_a, "enable_collision"_a = true)
|
||||
.def("addObject", &ModifyPlanningScene::addObject, R"(
|
||||
Add a CollisionObject_ to the planning scene
|
||||
|
||||
.. _CollisionObject: https://docs.ros.org/en/melodic/api/moveit_msgs/html/msg/CollisionObject.html
|
||||
|
||||
)", "collision_object"_a);
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<CurrentState, Stage>(m, "CurrentState", R"(
|
||||
Fetch the current PlanningScene state via the ``get_planning_scene`` service.
|
||||
|
||||
.. literalinclude:: ./../../../demo/scripts/current_state.py
|
||||
:language: python
|
||||
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("current state"));
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<FixedState, Stage>(m, "FixedState", R"(
|
||||
Spawn a pre-defined PlanningScene state.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-fixed-state>`
|
||||
for an implementation of a task hierarchy that makes use of the
|
||||
``FixedState`` stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def("setState", &FixedState::setState, R"(
|
||||
Use a planning scene pointer to specify which state the Fixed State
|
||||
stage should have.
|
||||
)", "scene"_a)
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("fixed state"));
|
||||
|
||||
#if 0
|
||||
.def("setState", [](FixedState& stage, const moveit_msg::PlanningScene& scene_msg) {
|
||||
// TODO: How to initialize the PlanningScene?
|
||||
planning_scene::PlanningScenePtr scene;
|
||||
scene->setPlanningSceneMsg(scene_msg);
|
||||
stage.setState(scene);
|
||||
})
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
;
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<ComputeIK, Stage>(m, "ComputeIK", R"(
|
||||
Wrapper for any pose generator stage to compute the inverse
|
||||
kinematics for a pose in Cartesian space.
|
||||
|
||||
The wrapper reads a ``target_pose`` from the interface state of
|
||||
solutions provided by the wrapped stage. This cartesian pose
|
||||
(``PoseStamped`` msg) is used as a goal pose for inverse
|
||||
kinematics.
|
||||
|
||||
Usually, the end effector's parent link or the group's tip link
|
||||
is used as the inverse kinematics frame, which should be
|
||||
moved to the goal frame. However, any other inverse kinematics
|
||||
frame can be defined (which is linked to the tip of the group).
|
||||
|
||||
Properties of the internally received ``InterfaceState`` can be
|
||||
forwarded to the newly generated, externally exposed ``InterfaceState``.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-compute-ik>`
|
||||
for an implementation of a task hierarchy that makes use of the
|
||||
``ComputeIK`` stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef", R"(
|
||||
str: Specify which end effector of the active planning group
|
||||
should be used.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("group", R"(
|
||||
str: Specify which planning group
|
||||
should be used.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("default_pose", R"(
|
||||
str: Default joint pose of the active group
|
||||
(defines cost of the inverse kinematics).
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<uint32_t>("max_ik_solutions", R"(
|
||||
int: Set the maximum number of inverse
|
||||
kinematic solutions thats should be generated.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<bool>("ignore_collisions", R"(
|
||||
bool: Specify if collisions with other members of
|
||||
the planning scene are allowed.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>("ik_frame", R"(
|
||||
PoseStamped_: Specify the frame with respect
|
||||
to which the inverse kinematics
|
||||
should be calculated.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _PoseStamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/PoseStamped.html
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>("target_pose", R"(
|
||||
PoseStamped_: Specify the pose on which
|
||||
the inverse kinematics should be
|
||||
calculated on. Since this property should
|
||||
almost always be set
|
||||
in the Interface State which is sent by the child,
|
||||
if possible, avoid setting it manually.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _PoseStamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/PoseStamped.html
|
||||
)")
|
||||
// methods of base class py::class_ need to be called last!
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&, Stage::pointer&&>(), "name"_a, "stage"_a);
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<MoveTo, PropagatingEitherWay, PyMoveTo<>>(m, "MoveTo", R"(
|
||||
Compute a trajectory between the robot state from the
|
||||
interface state of the preceeding stage and a specified
|
||||
goal.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-move-to>`
|
||||
for an implementation of a task hierarchy that makes use of the
|
||||
``MoveTo`` stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("group", R"(
|
||||
str: Planning group which should be utilized for planning and execution.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>("ik_frame", R"(
|
||||
PoseStamped_: IK reference frame for the goal pose
|
||||
|
||||
.. _PoseStamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/PoseStamped.html
|
||||
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<moveit_msgs::Constraints>("path_constraints", R"(
|
||||
Constraints_: Set path constraints via the corresponding moveit message type
|
||||
|
||||
.. _Constraints: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/moveit_msgs/html/msg/Constraints.html
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&, const solvers::PlannerInterfacePtr&>(), "name"_a, "planner"_a)
|
||||
.def("setGoal", py::overload_cast<const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&>(&MoveTo::setGoal), R"(
|
||||
Move link to a given PoseStamped_
|
||||
|
||||
.. _PoseStamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/PoseStamped.html
|
||||
)", "goal"_a)
|
||||
.def("setGoal", py::overload_cast<const geometry_msgs::PointStamped&>(&MoveTo::setGoal), R"(
|
||||
Move link to given PointStamped_, keeping current orientation
|
||||
|
||||
.. _PointStamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/PointStamped.html
|
||||
)", "goal"_a)
|
||||
.def("setGoal", py::overload_cast<const moveit_msgs::RobotState&>(&MoveTo::setGoal), R"(
|
||||
Move joints specified in RobotState_ to their target values
|
||||
|
||||
.. _RobotState: https://docs.ros.org/en/noetic/api/moveit_msgs/html/msg/RobotState.html
|
||||
)", "goal"_a)
|
||||
.def("setGoal", py::overload_cast<const std::map<std::string, double>&>(&MoveTo::setGoal), R"(
|
||||
Move joints by name to their mapped target value provided by dict goal argument
|
||||
)", "goal"_a)
|
||||
.def("setGoal", py::overload_cast<const std::string&>(&MoveTo::setGoal), R"(
|
||||
Move joint model group to given named pose provided as a str argument
|
||||
)", "goal"_a);
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<MoveRelative, PropagatingEitherWay, PyMoveRelative<>>(m, "MoveRelative", R"(
|
||||
Perform a Cartesian motion relative to some link.
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-move-relative>`
|
||||
for an implementation of a task hierarchy that makes use of the
|
||||
``MoveRelative`` stage.
|
||||
To implement your own propagtor logic on top of the ``MoveRelative`` class' functionality,
|
||||
you may derive from the stage. Take a look at the corresponding
|
||||
:ref:`How-To-Guide <subsubsec-howto-move-relative>`.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("group", R"(
|
||||
str: Planning group which should be utilized for planning and execution.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>("ik_frame", R"(
|
||||
PoseStamped_: IK reference frame for the goal pose.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _PoseStamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/PoseStamped.html
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<double>("min_distance", "float: Set the minimum distance to move")
|
||||
.property<double>("max_distance", "float: Set the maximum distance to move")
|
||||
.property<moveit_msgs::Constraints>("path_constraints", R"(
|
||||
Constraints_: These are the path constraints.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _Constraints: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/moveit_msgs/html/msg/Constraints.html
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&, const solvers::PlannerInterfacePtr&>(), "name"_a, "planner"_a)
|
||||
.def("setDirection", py::overload_cast<const geometry_msgs::TwistStamped&>(&MoveRelative::setDirection), R"(
|
||||
Perform twist motion on specified link.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _Twist: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/Twist.html
|
||||
)", "twist"_a)
|
||||
.def("setDirection", py::overload_cast<const geometry_msgs::Vector3Stamped&>(&MoveRelative::setDirection), R"(
|
||||
Translate link along given direction.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _Vector3Stamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/noetic/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/Vector3Stamped.html
|
||||
)", "direction"_a)
|
||||
.def("setDirection", py::overload_cast<const std::map<std::string, double>&>(&MoveRelative::setDirection), R"(
|
||||
Move specified joint variables by given amount.
|
||||
)", "joint_deltas"_a);
|
||||
|
||||
py::enum_<stages::Connect::MergeMode>(m, "MergeMode", R"(
|
||||
Define the merge strategy to use when performing planning operations
|
||||
with e.g. the connect stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.value("SEQUENTIAL", stages::Connect::MergeMode::SEQUENTIAL, "Store sequential trajectories")
|
||||
.value("WAYPOINTS", stages::Connect::MergeMode::WAYPOINTS, "Join trajectories by their waypoints");
|
||||
PropertyConverter<stages::Connect::MergeMode>();
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<Connect, Stage>(m, "Connect", R"(
|
||||
Connect arbitrary InterfaceStates by motion planning.
|
||||
You can specify the planning groups and the planners you
|
||||
want to utilize.
|
||||
|
||||
The states may differ in various planning groups.
|
||||
To connect both states, the planners provided for
|
||||
individual sub groups are applied in the specified order.
|
||||
Each planner only plan for joints within the corresponding
|
||||
planning group. Finally, an attempt is made to merge the
|
||||
sub trajectories of individual planning results.
|
||||
If this fails, the sequential planning result is returned.
|
||||
|
||||
For an example, see :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-connect>`.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&, const Connect::GroupPlannerVector&>(),
|
||||
"name"_a = std::string("connect"), "planners"_a);
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<FixCollisionObjects, Stage>(m, "FixCollisionObjects", R"(
|
||||
Test for collisions and find a correction for applicable objects.
|
||||
Move the objects out of the way along the correction direction.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-fix-collision-objects>`
|
||||
for an implementation of a task hierarchy that makes use of the
|
||||
``FixCollisionObjects`` stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<double>("max_penetration", R"(
|
||||
float: Cutoff length up to which collision objects get fixed.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("fix collisions"));
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<GeneratePlacePose, MonitoringGenerator>(m, "GeneratePlacePose", R"(
|
||||
GeneratePlacePose stage derives from monitoring generator and generates poses
|
||||
for the place pipeline. Notice that whilst GenerateGraspPose spawns poses with an
|
||||
``angle_delta`` intervall, GeneratePlacePose samples a fixed amount, which is dependent
|
||||
on the objects shape.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-generate-place-pose>`
|
||||
for a snippet that demonstrates usage of the `GeneratePlacePose` stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("object", R"(
|
||||
str: Name of the object in the planning scene, attached to the robot which should be placed
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef", "str: Name of the end effector that should be used for grasping")
|
||||
.property<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>("pose", R"(
|
||||
PoseStamped_: The pose where the object should be placed, i.e. states should be sampled
|
||||
|
||||
.. _PoseStamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/PoseStamped.html
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("Generate Place Pose"));
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<GenerateGraspPose, MonitoringGenerator>(m, "GenerateGraspPose", R"(
|
||||
GenerateGraspPose stage derives from monitoring generator and can
|
||||
be used to generate poses for grasping. Set the desired attributes
|
||||
of the grasp using the stages properties.
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-generate-grasp-pose>`
|
||||
for a snippet that demonstrates usage of the `GenerateGraspPose` stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("object", R"(
|
||||
str: Name of the Object in the planning scene, which should be grasped
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef", R"(
|
||||
str: Name of the end effector that should be used for grasping
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("pregrasp", "str: Name of the pre-grasp pose")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("grasp", "str: Name of the grasp pose")
|
||||
.property<double>("angle_delta", R"(
|
||||
float: Angular step distance in rad with which positions around the object are sampled.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a = std::string("Generate Grasp Pose"));
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<GeneratePose, MonitoringGenerator>(m, "GeneratePose", R"(
|
||||
Monitoring generator stage which can be used to generate a pose, based on solutions provided
|
||||
by the monitored stage.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`How-To-Guides <subsubsec-howto-fix-collision-objects>`
|
||||
for an implementation of a task hierarchy that makes use of the
|
||||
``GeneratePose`` stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>("pose", R"(
|
||||
PoseStamped_: Set the pose, which should be spawned on each new solution of the monitored stage.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _PoseStamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/PoseStamped.html
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string&>(), "name"_a);
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<Pick, SerialContainer>(m, "Pick", R"(
|
||||
The Pick stage is a specialization of the PickPlaceBase class, which
|
||||
wraps the pipeline to pick or place an object with a given end effector.
|
||||
|
||||
Picking consist of the following sub stages:
|
||||
|
||||
- Linearly approaching the object along an approach direction/twist "grasp" end effector posture
|
||||
- Attach the object
|
||||
- Lift along a given direction/twist
|
||||
|
||||
The end effector postures corresponding to pre-grasp and grasp as well
|
||||
as the end effector's cartesian pose needs to be provided by an external
|
||||
grasp stage.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`Pick and Place Tutorial <subsec-tut-pick-place>` for an in-depth look,
|
||||
as well as the :ref:`How-To Guide <subsubsec-howto-pick>` for a minimal implementation
|
||||
of a task hierarchy that makes use of the
|
||||
``Pick`` stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("object", "str: Name of object to pick")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef", "str: The End effector name")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef_frame", "str: Name of the end effector frame")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef_group", "str: Joint model group of the end effector")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef_parent_group", "str: Joint model group of the eef's parent")
|
||||
.def(py::init<Stage::pointer&&, const std::string&>(), "grasp_generator"_a,
|
||||
"name"_a = std::string("pick"))
|
||||
.def("setApproachMotion", &Pick::setApproachMotion, R"(
|
||||
The approaching motion towards the grasping state is represented
|
||||
by a twist message.
|
||||
Additionally specify the minimum and maximum allowed distances to travel.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _Twist: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/Twist.html
|
||||
)", "motion"_a, "min_distance"_a, "max_distance"_a)
|
||||
.def("setLiftMotion", py::overload_cast<const geometry_msgs::TwistStamped&, double, double>(&Pick::setLiftMotion), R"(
|
||||
The lifting motion away from the grasping state is represented by a twist message.
|
||||
Additionally specify the minimum and maximum allowed distances to travel.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _Twist: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/Twist.html
|
||||
)", "motion"_a, "min_distance"_a, "max_distance"_a)
|
||||
.def("setLiftMotion", py::overload_cast<const std::map<std::string, double>&>(&Pick::setLiftMotion), R"(
|
||||
The lifting motion away from the grasping state is represented by its destination as joint-value pairs
|
||||
)", "place"_a);
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<Place, SerialContainer>(m, "Place", R"(
|
||||
The Place stage is a specialization of the PickPlaceBase class, which
|
||||
wraps the pipeline to pick or place an object with a given end effector.
|
||||
|
||||
Placing consist of the inverse order of stages:
|
||||
|
||||
- Place down along a given direction
|
||||
- Detach the object
|
||||
- Linearly retract end effector
|
||||
|
||||
The end effector postures corresponding to pre-grasp and grasp as well
|
||||
as the end effector's Cartesian pose needs to be provided by an external
|
||||
grasp stage.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`Pick and Place Tutorial <subsec-tut-pick-place>` for an in-depth look,
|
||||
as well as the :ref:`How-To Guide <subsubsec-howto-place>` for a minimal implementation
|
||||
of a task hierarchy that makes use of the
|
||||
``Place`` stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("object", "str: Name of object to pick")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef", "str: The End effector name")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef_frame", "str: Name of the end effector frame")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef_group", "str: Joint model group of the end effector")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef_parent_group", "str: Joint model group of the eef's parent")
|
||||
.def("setRetractMotion", &Place::setRetractMotion, R"(
|
||||
The retract motion towards the final state is represented
|
||||
by a Twist_ message. Additionally specify the minimum and
|
||||
maximum allowed distances to travel.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _Twist: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/Twist.html
|
||||
)", "motion"_a, "min_distance"_a, "max_distance"_a)
|
||||
.def("setPlaceMotion", py::overload_cast<const geometry_msgs::TwistStamped&, double, double>(&Place::setPlaceMotion), R"(
|
||||
The object-placing motion towards the final state is represented by a twist message.
|
||||
Additionally specify the minimum and maximum allowed distances to travel.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _Twist: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/Twist.html
|
||||
)", "motion"_a, "min_distance"_a, "max_distance"_a )
|
||||
.def("setPlaceMotion", py::overload_cast<const std::map<std::string, double>&>(&Place::setPlaceMotion), R"(
|
||||
The placing motion to the final state is represented by its destination as joint-value pairs
|
||||
)", "joints"_a )
|
||||
.def(py::init<Stage::pointer&&, const std::string&>(), "place_generator"_a,
|
||||
"name"_a = std::string("place"));
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<SimpleGraspBase, SerialContainer>(m, "SimpleGraspBase", "Abstract base class for grasping and releasing")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("eef", "str: The end effector of the robot")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("object", "str: The object to grasp (Must be present in the planning scene)")
|
||||
.property<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>("ik_frame", R"(
|
||||
PoseStamped_: Set the frame for which the inverse kinematics is calculated
|
||||
with respect to each pose generated by the pose_generator.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _PoseStamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/PoseStamped.html
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def<void (SimpleGraspBase::*)(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&)>("setIKFrame", &SimpleGraspBase::setIKFrame, R"(
|
||||
Set the frame as a PoseStamped_ for which the inverse kinematics are calculated with respect to
|
||||
each pose generated by the pose_generator.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _PoseStamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/PoseStamped.html
|
||||
)", "transform"_a)
|
||||
.def<void (SimpleGraspBase::*)(const Eigen::Isometry3d&, const std::string&)>("setIKFrame", &SimpleGraspBase::setIKFrame, R"(
|
||||
Set the frame as a PoseStamped_ for which the inverse kinematics are calculated
|
||||
with respect to each pose generated by the pose_generator.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _PoseStamped: https://docs.ros.org/en/api/geometry_msgs/html/msg/PoseStamped.html
|
||||
)", "pose"_a, "link"_a)
|
||||
.def<void (SimpleGraspBase::*)(const std::string&)>("setIKFrame", &SimpleGraspBase::setIKFrame, R"(
|
||||
Set the frame for which the inverse kinematics are calculated
|
||||
with respect to each pose generated by the pose_generator.
|
||||
)", "link"_a)
|
||||
.def("setMaxIKSolutions", &SimpleGraspBase::setMaxIKSolutions, R"(
|
||||
Set the maximum number of inverse kinematics solutions that should be computed.
|
||||
)", "max_ik_solutions"_a)
|
||||
;
|
||||
properties::class_<SimpleGrasp, SimpleGraspBase>(m, "SimpleGrasp", R"(
|
||||
Specialization of SimpleGraspBase to realize grasping.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`Pick and Place Tutorial <subsec-tut-pick-place>` for an in-depth look,
|
||||
as well as the :ref:`How-To Guide <subsubsec-howto-simplegrasp>` for a minimal implementation
|
||||
of a task hierarchy that makes use of the
|
||||
``SimpleGrasp`` stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.def(py::init<Stage::pointer&&, const std::string&>(), "pose_generator"_a,
|
||||
"name"_a = std::string("grasp"));
|
||||
|
||||
properties::class_<SimpleUnGrasp, SimpleGraspBase>(m, "SimpleUnGrasp", R"(
|
||||
Specialization of SimpleGraspBase to realize ungrasping
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the :ref:`Pick and Place Tutorial <subsec-tut-pick-place>` for an in-depth look,
|
||||
as well as the :ref:`How-To Guide <subsubsec-howto-simplegrasp>` for a minimal implementation
|
||||
of a task hierarchy that makes use of the
|
||||
``SimpleUnGrasp`` stage.
|
||||
)")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("pregrasp", "str: Name of the pre-grasp pose")
|
||||
.property<std::string>("grasp", "str: Name of the grasp pose")
|
||||
.def(py::init<Stage::pointer&&, const std::string&>(), "pose_generator"_a,
|
||||
"name"_a = std::string("ungrasp"));
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace python
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
84
core/python/bindings/src/stages.h
Normal file
84
core/python/bindings/src/stages.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
/*********************************************************************
|
||||
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2020, Bielefeld University
|
||||
* All rights reserved.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
|
||||
* are met:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
|
||||
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
|
||||
* with the distribution.
|
||||
* * Neither the name of Bielefeld University nor the names of its
|
||||
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
|
||||
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
|
||||
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
|
||||
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
|
||||
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
|
||||
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
|
||||
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
|
||||
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
*********************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#pragma once
|
||||
|
||||
#include "core.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/stages/move_relative.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/task_constructor/stages/move_to.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/** Trampoline classes to allow inheritance in Python (overriding virtual functions) */
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace task_constructor {
|
||||
namespace stages {
|
||||
|
||||
template <class T = MoveTo>
|
||||
class PyMoveTo : public PyPropagatingEitherWay<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using PyPropagatingEitherWay<T>::PyPropagatingEitherWay;
|
||||
void computeForward(const InterfaceState& from_state) override {
|
||||
// pass InterfaceState as pointer to trigger passing by reference
|
||||
PYBIND11_OVERRIDE_IMPL(void, T, "computeForward", &from_state);
|
||||
return T::computeForward(from_state);
|
||||
}
|
||||
void computeBackward(const InterfaceState& to_state) override {
|
||||
// pass InterfaceState as pointer to trigger passing by reference
|
||||
PYBIND11_OVERRIDE_IMPL(void, T, "computeBackward", &to_state);
|
||||
return T::computeBackward(to_state);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <class T = MoveRelative>
|
||||
class PyMoveRelative : public PyPropagatingEitherWay<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using PyPropagatingEitherWay<T>::PyPropagatingEitherWay;
|
||||
void computeForward(const InterfaceState& from_state) override {
|
||||
// pass InterfaceState as pointer to trigger passing by reference
|
||||
PYBIND11_OVERRIDE_IMPL(void, T, "computeForward", &from_state);
|
||||
return T::computeForward(from_state);
|
||||
}
|
||||
void computeBackward(const InterfaceState& to_state) override {
|
||||
// pass InterfaceState as pointer to trigger passing by reference
|
||||
PYBIND11_OVERRIDE_IMPL(void, T, "computeBackward", &to_state);
|
||||
return T::computeBackward(to_state);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace stages
|
||||
} // namespace task_constructor
|
||||
} // namespace moveit
|
||||
1
core/python/pybind11
Submodule
1
core/python/pybind11
Submodule
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
Subproject commit 4070a64f867c60842476f74a2212110ea5e05230
|
||||
2
core/python/src/__init__.py
Normal file
2
core/python/src/__init__.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
# https://packaging.python.org/guides/packaging-namespace-packages/#pkgutil-style-namespace-packages
|
||||
__path__ = __import__("pkgutil").extend_path(__path__, __name__)
|
||||
1
core/python/src/python_tools/__init__.py
Normal file
1
core/python/src/python_tools/__init__.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
from pymoveit_python_tools import *
|
||||
3
core/python/src/task_constructor/__init__.py
Normal file
3
core/python/src/task_constructor/__init__.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
from . import core, stages
|
||||
|
||||
__doc__ = "top-level module of MoveIt Task constructor"
|
||||
3
core/python/src/task_constructor/core.py
Normal file
3
core/python/src/task_constructor/core.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
from pymoveit_mtc.core import *
|
||||
|
||||
__doc__ = "Provides wrappers for :doc:`core C++ classes <pymoveit_mtc.core>`."
|
||||
3
core/python/src/task_constructor/stages.py
Normal file
3
core/python/src/task_constructor/stages.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
from pymoveit_mtc.stages import *
|
||||
|
||||
__doc__ = "Provides wrappers for :doc:`stage C++ classes <pymoveit_mtc.stages>`."
|
||||
69
core/python/test/rostest_mtc.py
Executable file
69
core/python/test/rostest_mtc.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
import rostest
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped, Pose
|
||||
from geometry_msgs.msg import Vector3Stamped, Vector3
|
||||
from std_msgs.msg import Header
|
||||
import rospy
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Test(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
PLANNING_GROUP = "manipulator"
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def setUpClass(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def tearDown(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def test_MoveRelative(self):
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
task.add(stages.CurrentState("current"))
|
||||
move = stages.MoveRelative("move", core.JointInterpolationPlanner())
|
||||
move.group = self.PLANNING_GROUP
|
||||
move.setDirection({"joint_1": 0.2, "joint_2": 0.4})
|
||||
task.add(move)
|
||||
|
||||
task.enableIntrospection()
|
||||
task.init()
|
||||
task.plan()
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(task.solutions), 1)
|
||||
for s in task.solutions:
|
||||
print(s)
|
||||
s = task.solutions[0]
|
||||
task.execute(s)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_Merger(self):
|
||||
cartesian = core.CartesianPath()
|
||||
|
||||
def createDisplacement(group, displacement):
|
||||
move = stages.MoveRelative("displace", cartesian)
|
||||
move.group = group
|
||||
move.ik_frame = PoseStamped(header=Header(frame_id="tool0"))
|
||||
dir = Vector3Stamped(header=Header(frame_id="base_link"), vector=Vector3(*displacement))
|
||||
move.setDirection(dir)
|
||||
move.restrictDirection(stages.MoveRelative.Direction.FORWARD)
|
||||
return move
|
||||
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
task.add(stages.CurrentState("current"))
|
||||
merger = core.Merger("merger")
|
||||
merger.insert(createDisplacement(self.PLANNING_GROUP, [-0.2, 0, 0]))
|
||||
merger.insert(createDisplacement(self.PLANNING_GROUP, [0.2, 0, 0]))
|
||||
task.add(merger)
|
||||
|
||||
task.enableIntrospection()
|
||||
task.init()
|
||||
self.assertFalse(task.plan())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
roscpp_init("test_mtc")
|
||||
rostest.rosrun("mtc", "base", Test)
|
||||
5
core/python/test/rostest_mtc.test
Normal file
5
core/python/test/rostest_mtc.test
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
<launch>
|
||||
<include file="$(find moveit_resources_fanuc_moveit_config)/launch/test_environment.launch" />
|
||||
<test pkg="moveit_task_constructor_core" type="rostest_mtc.py" test-name="rostest_mtc" time-limit="60" args="" />
|
||||
<test pkg="moveit_task_constructor_core" type="rostest_trampoline.py" test-name="rostest_trampoline" time-limit="60" args="" />
|
||||
</launch>
|
||||
135
core/python/test/rostest_trampoline.py
Executable file
135
core/python/test/rostest_trampoline.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
import rostest
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from moveit.core.planning_scene import PlanningScene
|
||||
from geometry_msgs.msg import Vector3Stamped, Vector3
|
||||
from std_msgs.msg import Header
|
||||
|
||||
PLANNING_GROUP = "manipulator"
|
||||
|
||||
pybind11_versions = [
|
||||
k for k in __builtins__.__dict__.keys() if k.startswith("__pybind11_internals_v")
|
||||
]
|
||||
incompatible_pybind11_msg = "MoveIt and MTC use incompatible pybind11 versions: " + "\n- ".join(
|
||||
pybind11_versions
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PyGenerator(core.Generator):
|
||||
"""Implements a custom 'Generator' stage."""
|
||||
|
||||
max_calls = 3
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, name="Generator"):
|
||||
core.Generator.__init__(self, name)
|
||||
self.reset()
|
||||
|
||||
def init(self, robot_model):
|
||||
self.ps = PlanningScene(robot_model)
|
||||
|
||||
def reset(self):
|
||||
core.Generator.reset(self)
|
||||
self.num = self.max_calls
|
||||
|
||||
def canCompute(self):
|
||||
return self.num > 0
|
||||
|
||||
def compute(self):
|
||||
self.num = self.num - 1
|
||||
self.spawn(core.InterfaceState(self.ps), self.num)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PyMonitoringGenerator(core.MonitoringGenerator):
|
||||
"""Implements a custom 'MonitoringGenerator' stage."""
|
||||
|
||||
solution_multiplier = 2
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, name="MonitoringGenerator"):
|
||||
core.MonitoringGenerator.__init__(self, name)
|
||||
self.reset()
|
||||
|
||||
def reset(self):
|
||||
core.MonitoringGenerator.reset(self)
|
||||
self.upstream_solutions = list()
|
||||
|
||||
def onNewSolution(self, sol):
|
||||
self.upstream_solutions.append(sol)
|
||||
|
||||
def canCompute(self):
|
||||
return bool(self.upstream_solutions)
|
||||
|
||||
def compute(self):
|
||||
scene = self.upstream_solutions.pop(0).end.scene
|
||||
for i in range(self.solution_multiplier):
|
||||
self.spawn(core.InterfaceState(scene), i)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PyMoveRelX(stages.MoveRelative):
|
||||
"""Implements a custom propagator stage."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, x, planner, name="Move ±x"):
|
||||
stages.MoveRelative.__init__(self, name, planner)
|
||||
self.group = PLANNING_GROUP
|
||||
self.ik_frame = "tool0"
|
||||
self.setDirection(
|
||||
Vector3Stamped(header=Header(frame_id="base_link"), vector=Vector3(x, 0, 0))
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def computeForward(self, from_state):
|
||||
return stages.MoveRelative.computeForward(self, from_state)
|
||||
|
||||
def computeBackward(self, to_state):
|
||||
return stages.MoveRelative.computeBackward(self, to_state)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestTrampolines(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def setUp(self):
|
||||
self.cartesian = core.CartesianPath()
|
||||
self.jointspace = core.JointInterpolationPlanner()
|
||||
|
||||
def create(self, *stages):
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
task.enableIntrospection()
|
||||
for stage in stages:
|
||||
task.add(stage)
|
||||
return task
|
||||
|
||||
def plan(self, task, expected_solutions=None, wait=False):
|
||||
task.plan()
|
||||
if expected_solutions is not None:
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(task.solutions), expected_solutions)
|
||||
if wait:
|
||||
input("Waiting for any key (allows inspection in rviz)")
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(len(pybind11_versions) > 1, incompatible_pybind11_msg)
|
||||
def test_generator(self):
|
||||
task = self.create(PyGenerator())
|
||||
self.plan(task, expected_solutions=PyGenerator.max_calls)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(len(pybind11_versions) > 1, incompatible_pybind11_msg)
|
||||
def test_monitoring_generator(self):
|
||||
task = self.create(
|
||||
stages.CurrentState("current"),
|
||||
stages.Connect(planners=[(PLANNING_GROUP, self.jointspace)]),
|
||||
PyMonitoringGenerator("generator"),
|
||||
)
|
||||
task["generator"].setMonitoredStage(task["current"])
|
||||
self.plan(task, expected_solutions=PyMonitoringGenerator.solution_multiplier)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_propagator(self):
|
||||
task = self.create(
|
||||
PyMoveRelX(-0.2, self.cartesian),
|
||||
stages.CurrentState(),
|
||||
PyMoveRelX(+0.2, self.cartesian),
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.plan(task, expected_solutions=1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
roscpp_init("test_mtc")
|
||||
rostest.rosrun("mtc", "trampoline", TestTrampolines)
|
||||
347
core/python/test/test_mtc.py
Normal file
347
core/python/test/test_mtc.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,347 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import unittest, sys
|
||||
from geometry_msgs.msg import Pose, PoseStamped, PointStamped, TwistStamped, Vector3Stamped
|
||||
from moveit_msgs.msg import RobotState, Constraints, MotionPlanRequest
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestPropertyMap(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
super(TestPropertyMap, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
self.props = core.PropertyMap()
|
||||
|
||||
def _check(self, name, value):
|
||||
self.props[name] = value
|
||||
self.assertEqual(self.props[name], value)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_assign(self):
|
||||
self._check("double", 3.14)
|
||||
self._check("long", 42)
|
||||
self._check("long", 13)
|
||||
self._check("bool", True)
|
||||
self._check("bool", False)
|
||||
self._check("string", "anything")
|
||||
self._check("pose", PoseStamped())
|
||||
# MotionPlanRequest is not registered as property type and should raise
|
||||
self.assertRaises(TypeError, self._check, "request", MotionPlanRequest())
|
||||
|
||||
def test_assign_in_reference(self):
|
||||
planner = core.PipelinePlanner()
|
||||
props = planner.properties
|
||||
|
||||
props["goal_joint_tolerance"] = 3.14
|
||||
self.assertEqual(props["goal_joint_tolerance"], 3.14)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(planner.goal_joint_tolerance, 3.14)
|
||||
|
||||
planner.goal_joint_tolerance = 2.71
|
||||
self.assertEqual(props["goal_joint_tolerance"], 2.71)
|
||||
|
||||
props["planner"] = "planner"
|
||||
self.assertEqual(props["planner"], "planner")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(planner.planner, "planner")
|
||||
|
||||
props["double"] = 3.14
|
||||
a = props
|
||||
props["double"] = 2.71
|
||||
self.assertEqual(a["double"], 2.71)
|
||||
|
||||
planner.planner = "other"
|
||||
self.assertEqual(props["planner"], "other")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(planner.planner, "other")
|
||||
|
||||
del planner
|
||||
# We can still access props, because actual destruction of planner is delayed
|
||||
self.assertEqual(props["goal_joint_tolerance"], 2.71)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(props["planner"], "other")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_iter(self):
|
||||
# assign values so we can iterate over them
|
||||
self.props["double"] = 3.14
|
||||
self.props["bool"] = True
|
||||
keys = [v for v in self.props]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(keys), 2)
|
||||
items = [(k, v) for (k, v) in self.props.items()]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(keys, [k for (k, v) in items])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_update(self):
|
||||
self.props["double"] = 3.14
|
||||
self.props.update({"double": 2.72, "bool": True})
|
||||
self.props.update({})
|
||||
self.assertEqual(self.props["double"], 2.72)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(self.props["bool"], True)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_expose(self):
|
||||
self.props["double"] = 3.14
|
||||
|
||||
other = core.PropertyMap()
|
||||
self.props.exposeTo(other, "double")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(other["double"], self.props["double"])
|
||||
|
||||
self.props.exposeTo(other, "double", "float")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(other["float"], self.props["double"])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestModifyPlanningScene(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
super(TestModifyPlanningScene, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
self.mps = stages.ModifyPlanningScene("mps")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_attach_objects_invalid_args(self):
|
||||
for value in [None, 1, 1.5, {}]:
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, self.mps.attachObjects, value, "link")
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, self.mps.attachObjects, value, "link", True)
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, self.mps.attachObjects, value, "link", False)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_attach_objects_valid_args(self):
|
||||
self.mps.attachObject("object", "link")
|
||||
self.mps.detachObject("object", "link")
|
||||
|
||||
self.mps.attachObjects("object", "link")
|
||||
self.mps.detachObjects("object", "link")
|
||||
self.mps.attachObjects("object", "link", True)
|
||||
self.mps.attachObjects("object", "link", False)
|
||||
|
||||
self.mps.attachObjects([], "link")
|
||||
self.mps.attachObjects(["object"], "link")
|
||||
self.mps.attachObjects(["object1", "object2", "object3"], "link")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_allow_collisions(self):
|
||||
self.mps.allowCollisions("first", "second")
|
||||
self.mps.allowCollisions("first", "second", True)
|
||||
self.mps.allowCollisions("first", "second", False)
|
||||
|
||||
self.mps.allowCollisions(["first"], ["second"])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestStages(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
super(TestStages, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
self.planner = core.PipelinePlanner()
|
||||
|
||||
def _check(self, stage, name, value):
|
||||
self._check_assign(stage, name, value)
|
||||
self._check_invalid_args(stage, name, type(value))
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_assign(self, stage, name, value):
|
||||
setattr(stage, name, value)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(getattr(stage, name), value)
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_invalid_args(self, stage, name, target_type):
|
||||
"""Check some basic types to raise an ArgumentError when assigned"""
|
||||
for value in [None, 1, 1.0, "string", [], {}, set()]:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
target_type(value)
|
||||
continue # ignore values that are implicitly convertible to target_type
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
setattr(stage, name, value)
|
||||
except TypeError:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
except:
|
||||
msg = "Assigning {} did raise wrong exception: {}"
|
||||
self.fail(msg.format(value, sys.exc_info()[0]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if value == "string" and target_type is PoseStamped:
|
||||
continue # string is convertible to PoseStamped
|
||||
msg = "Assigning {} did not raise an exception, result: {}"
|
||||
self.fail(msg.format(value, getattr(stage, name)))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_CurrentState(self):
|
||||
stage = stages.CurrentState("current")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_FixedState(self):
|
||||
stage = stages.FixedState("fixed")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_ComputeIK(self):
|
||||
generator_stage = stages.GeneratePose("generator")
|
||||
stage = stages.ComputeIK("IK", generator_stage)
|
||||
|
||||
self._check(stage, "timeout", 0.5)
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef", "eef")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "group", "group")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "default_pose", "default_pose")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "max_ik_solutions", 1)
|
||||
self.assertRaises(TypeError, self._check_assign, stage, "max_ik_solutions", -1)
|
||||
self._check(stage, "ignore_collisions", False)
|
||||
self._check(stage, "ignore_collisions", True)
|
||||
self._check(stage, "ik_frame", PoseStamped())
|
||||
self._check(stage, "target_pose", PoseStamped())
|
||||
self._check(stage, "forwarded_properties", ["name1", "name2", "name3"])
|
||||
stage.forwarded_properties = "name"
|
||||
self.assertRaises(TypeError, self._check_assign, stage, "forwarded_properties", [1, 2])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_MoveTo(self):
|
||||
stage = stages.MoveTo("move", self.planner)
|
||||
|
||||
self._check(stage, "group", "group")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "ik_frame", PoseStamped())
|
||||
self._check(stage, "path_constraints", Constraints())
|
||||
stage.setGoal(PoseStamped())
|
||||
stage.setGoal(PointStamped())
|
||||
stage.setGoal(RobotState())
|
||||
stage.setGoal("named pose")
|
||||
stage.setGoal(dict(joint1=1.0, joint2=2.0))
|
||||
self._check(stage, "path_constraints", Constraints())
|
||||
|
||||
def test_MoveRelative(self):
|
||||
stage = stages.MoveRelative("move", self.planner)
|
||||
|
||||
self._check(stage, "group", "group")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "ik_frame", PoseStamped())
|
||||
self._check(stage, "min_distance", 0.5)
|
||||
self._check(stage, "max_distance", 0.25)
|
||||
self._check(stage, "path_constraints", Constraints())
|
||||
stage.setDirection(TwistStamped())
|
||||
stage.setDirection(Vector3Stamped())
|
||||
stage.setDirection({"joint": 0.1})
|
||||
|
||||
def test_Connect(self):
|
||||
planner = core.PipelinePlanner()
|
||||
stage = stages.Connect("connect", [("group1", planner), ("group2", planner)])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_FixCollisionObjects(self):
|
||||
stage = stages.FixCollisionObjects("collision")
|
||||
|
||||
self._check(stage, "max_penetration", 0.5)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_GenerateGraspPose(self):
|
||||
stage = stages.GenerateGraspPose("generate_grasp_pose")
|
||||
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef", "eef")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "pregrasp", "pregrasp")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "object", "object")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "angle_delta", 0.5)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_GeneratePose(self):
|
||||
stage = stages.GeneratePose("generate_pose")
|
||||
|
||||
self._check(stage, "pose", PoseStamped())
|
||||
|
||||
def test_Pick(self):
|
||||
generator_stage = stages.GeneratePose("generator")
|
||||
stage = stages.Pick(generator_stage, "pick")
|
||||
|
||||
self._check(stage, "object", "object")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef", "eef")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef_frame", "eef_frame")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef_group", "eef_group")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef_parent_group", "eef_parent_group")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_Place(self):
|
||||
generator_stage = stages.GeneratePose("generator")
|
||||
stage = stages.Place(generator_stage, "place")
|
||||
|
||||
self._check(stage, "object", "object")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef", "eef")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef_frame", "eef_frame")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef_group", "eef_group")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef_parent_group", "eef_parent_group")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_SimpleGrasp(self):
|
||||
stage = stages.SimpleGrasp(stages.GenerateGraspPose("grasp"))
|
||||
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef", "eef")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "object", "object")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_SimpleUnGrasp(self):
|
||||
stage = stages.SimpleUnGrasp(stages.GenerateGraspPose("ungrasp"))
|
||||
|
||||
self._check(stage, "eef", "eef")
|
||||
self._check(stage, "object", "object")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_PropertyMaps(self):
|
||||
for name in dir(stages):
|
||||
if name.startswith("__") or name.endswith("__"):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
stage = getattr(stages, name)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
props = stage().properties
|
||||
except:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
for p in props:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
except Exception as ex:
|
||||
print("error in class {}: {}".format(stage, ex))
|
||||
raise
|
||||
|
||||
def test_CostTerm(self):
|
||||
stage = stages.CurrentState()
|
||||
weights = {"joint_{}".format(i + 1): 1.0 for i in range(6)}
|
||||
costs = core.PathLength(weights)
|
||||
stage.setCostTerm(costs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BaseTestCases:
|
||||
class ContainerTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def __init__(self, ContainerType, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
super(BaseTestCases.ContainerTest, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
self.ContainerType = ContainerType
|
||||
self.container = container = ContainerType()
|
||||
container.add(stages.CurrentState("1"))
|
||||
container.add(stages.CurrentState("2"))
|
||||
container.add(stages.CurrentState("3"))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_move(self):
|
||||
container = self.ContainerType()
|
||||
stage = stages.CurrentState()
|
||||
container.add(stage)
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
|
||||
stage.name
|
||||
|
||||
def test_access_by_name(self):
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(IndexError):
|
||||
self.container["unknown"]
|
||||
|
||||
child = self.container["2"]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(child.name, "2")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_access_by_iterator(self):
|
||||
self.assertEqual([child.name for child in self.container], ["1", "2", "3"])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_access_by_index(self):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(self.container[0].name, "1")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(self.container[1].name, "2")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(self.container[-1].name, "3")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(self.container[-2].name, "2")
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(IndexError):
|
||||
self.container[3]
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(IndexError):
|
||||
self.container[-4]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestSerial(BaseTestCases.ContainerTest):
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
super(TestSerial, self).__init__(core.SerialContainer, *args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestTask(BaseTestCases.ContainerTest):
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
super(TestTask, self).__init__(core.Task, *args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def test(self):
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
current = stages.CurrentState("current")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(current.name, "current")
|
||||
current.timeout = 1.23
|
||||
self.assertEqual(current.timeout, 1.23)
|
||||
|
||||
task.add(current)
|
||||
|
||||
# ownership of current was passed to task
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
|
||||
current.name
|
||||
|
||||
task.add(stages.Connect("connect", []))
|
||||
task.add(stages.FixedState())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
unittest.main()
|
||||
10
core/rosdoc.yaml
Normal file
10
core/rosdoc.yaml
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
- builder: sphinx
|
||||
name: Python API
|
||||
output_dir: python
|
||||
sphinx_root_dir: doc
|
||||
- builder: doxygen
|
||||
name: C++ API
|
||||
output_dir: cpp
|
||||
file_patterns: "*.c *.cpp *.h *.cc *.hh *.dox"
|
||||
exclude_patterns: "*/core/python/pybind11/* */core/python/bindings/* */test/* "
|
||||
exclude_symbols: "*Private class_ declval*"
|
||||
@ -342,6 +342,12 @@ Stage* ContainerBase::findChild(const std::string& name) const {
|
||||
return nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Stage* ContainerBase::operator[](int index) const {
|
||||
auto impl = pimpl();
|
||||
auto it = impl->childByIndex(index, false);
|
||||
return it != impl->children().end() ? it->get() : nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool ContainerBase::traverseChildren(const ContainerBase::StageCallback& processor) const {
|
||||
return pimpl()->traverseStages(processor, 0, 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1054,6 +1060,7 @@ void FallbacksPrivateConnect::onNewFailure(const Stage& child, const InterfaceSt
|
||||
// ... thus we can use std::next(active_) to find the next child
|
||||
auto next = std::next(active_);
|
||||
|
||||
// NOLINTNEXTLINE(readability-identifier-naming)
|
||||
auto findIteratorFor = [](const InterfaceState* state, const Interface& interface) {
|
||||
auto it = std::find(interface.begin(), interface.end(), state);
|
||||
assert(it != interface.end());
|
||||
@ -1063,9 +1070,9 @@ void FallbacksPrivateConnect::onNewFailure(const Stage& child, const InterfaceSt
|
||||
if (next != children().end()) { // pass job to next child
|
||||
auto next_con = static_cast<ConnectingPrivate*>(const_cast<StagePrivate*>((*next)->pimpl()));
|
||||
auto first_con = static_cast<const ConnectingPrivate*>(children().front()->pimpl());
|
||||
auto fromIt = findIteratorFor(from, *first_con->starts());
|
||||
auto toIt = findIteratorFor(to, *first_con->ends());
|
||||
next_con->pending.insert(std::make_pair(fromIt, toIt));
|
||||
auto from_it = findIteratorFor(from, *first_con->starts());
|
||||
auto to_it = findIteratorFor(to, *first_con->ends());
|
||||
next_con->pending.insert(std::make_pair(from_it, to_it));
|
||||
} else // or report failure to parent
|
||||
parent()->pimpl()->onNewFailure(*me(), from, to);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,6 +40,7 @@
|
||||
#include <moveit/collision_detection/collision_common.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/robot_trajectory/robot_trajectory.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/planning_scene/planning_scene.h>
|
||||
#include <moveit/robot_state/conversions.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -106,17 +107,23 @@ double Constant::operator()(const WrappedSolution& /*s*/, std::string& /*comment
|
||||
return cost;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
PathLength::PathLength(std::vector<std::string> joints) {
|
||||
for (auto& j : joints)
|
||||
this->joints.emplace(std::move(j), 1.0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
double PathLength::operator()(const SubTrajectory& s, std::string& /*comment*/) const {
|
||||
const auto& traj = s.trajectory();
|
||||
|
||||
if (traj == nullptr || traj->getWayPointCount() == 0)
|
||||
return 0.0;
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<const moveit::core::JointModel*> joint_models;
|
||||
joint_models.reserve(joints.size());
|
||||
std::map<const moveit::core::JointModel*, double> weights;
|
||||
const auto& first_waypoint = traj->getWayPoint(0);
|
||||
for (auto& joint : joints) {
|
||||
joint_models.push_back(first_waypoint.getJointModel(joint));
|
||||
for (auto& joint_weight : joints) {
|
||||
const moveit::core::JointModel* jm = first_waypoint.getJointModel(joint_weight.first);
|
||||
if (jm)
|
||||
weights.emplace(jm, joint_weight.second);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
double path_length{ 0.0 };
|
||||
@ -126,14 +133,67 @@ double PathLength::operator()(const SubTrajectory& s, std::string& /*comment*/)
|
||||
if (joints.empty()) {
|
||||
path_length += last.distance(curr);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for (const auto& model : joint_models) {
|
||||
path_length += last.distance(curr, model);
|
||||
for (const auto& item : weights) {
|
||||
path_length += item.second * last.distance(curr, item.first);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return path_length;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
DistanceToReference::DistanceToReference(const moveit_msgs::msg::RobotState& ref, Mode m,
|
||||
std::map<std::string, double> w)
|
||||
: reference(ref), weights(std::move(w)), mode(m) {}
|
||||
|
||||
DistanceToReference::DistanceToReference(const std::map<std::string, double>& ref, Mode m,
|
||||
std::map<std::string, double> w)
|
||||
: weights(std::move(w)), mode(m) {
|
||||
reference.joint_state.name.reserve(ref.size());
|
||||
reference.joint_state.position.reserve(ref.size());
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto& item : ref) {
|
||||
reference.joint_state.name.push_back(item.first);
|
||||
reference.joint_state.position.push_back(item.second);
|
||||
}
|
||||
reference.is_diff = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
double DistanceToReference::operator()(const SubTrajectory& s, std::string& /*comment*/) const {
|
||||
const auto& state = (mode == Mode::END_INTERFACE) ? s.end() : s.start();
|
||||
const auto& traj = s.trajectory();
|
||||
|
||||
moveit::core::RobotState ref_state = state->scene()->getCurrentState();
|
||||
moveit::core::robotStateMsgToRobotState(reference, ref_state, false);
|
||||
|
||||
std::map<const moveit::core::JointModel*, double> w;
|
||||
for (auto& item : weights) {
|
||||
const moveit::core::JointModel* jm = ref_state.getJointModel(item.first);
|
||||
if (jm)
|
||||
w.emplace(jm, item.second);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto distance = [this, &ref_state, &w](const moveit::core::RobotState& state) {
|
||||
if (weights.empty()) {
|
||||
return ref_state.distance(state);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
double accumulated = 0.0;
|
||||
for (const auto& item : w)
|
||||
accumulated += item.second * ref_state.distance(state, item.first);
|
||||
return accumulated;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
if (mode == Mode::START_INTERFACE || mode == Mode::END_INTERFACE || (mode == Mode::AUTO && (traj == nullptr))) {
|
||||
return distance(state->scene()->getCurrentState());
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
double accumulated = 0.0;
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < traj->getWayPointCount(); ++i)
|
||||
accumulated += distance(traj->getWayPoint(i));
|
||||
accumulated /= traj->getWayPointCount();
|
||||
return accumulated;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
double TrajectoryDuration::operator()(const SubTrajectory& s, std::string& /*comment*/) const {
|
||||
return s.trajectory() ? s.trajectory()->getDuration() : 0.0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -218,8 +218,8 @@ const SolutionBase* Introspection::solutionFromId(uint id) const {
|
||||
return it->second;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool Introspection::getSolution(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::srv::GetSolution::Request::SharedPtr req,
|
||||
const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::srv::GetSolution::Response::SharedPtr res) {
|
||||
bool Introspection::getSolution(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::srv::GetSolution::Request::SharedPtr& req,
|
||||
const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::srv::GetSolution::Response::SharedPtr& res) {
|
||||
const SolutionBase* solution = solutionFromId(req->solution_id);
|
||||
if (!solution)
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,6 +40,7 @@
|
||||
#include <boost/format.hpp>
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
#include <rclcpp/logging.hpp>
|
||||
#include <rclcpp/clock.hpp>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace moveit {
|
||||
namespace task_constructor {
|
||||
@ -73,7 +74,9 @@ public:
|
||||
const Entry& entry(const std::type_index& type_index) const {
|
||||
auto it = types_.find(type_index);
|
||||
if (it == types_.end()) {
|
||||
RCLCPP_ERROR_STREAM(LOGGER, "Unregistered type: " << type_index.name());
|
||||
rclcpp::Clock steady_clock(RCL_STEADY_TIME);
|
||||
RCLCPP_WARN_STREAM_THROTTLE(LOGGER, steady_clock, 10'000,
|
||||
"Unregistered property type: " << boost::core::demangle(type_index.name()));
|
||||
return dummy_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return it->second;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -616,6 +616,14 @@ template void PropagatingEitherWay::send<Interface::FORWARD>(const InterfaceStat
|
||||
template void PropagatingEitherWay::send<Interface::BACKWARD>(const InterfaceState& start, InterfaceState&& end,
|
||||
SubTrajectory&& trajectory);
|
||||
|
||||
void PropagatingEitherWay::computeForward(const InterfaceState& from) {
|
||||
computeGeneric<Interface::FORWARD>(from);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void PropagatingEitherWay::computeBackward(const InterfaceState& to) {
|
||||
computeGeneric<Interface::BACKWARD>(to);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <Interface::Direction dir>
|
||||
void PropagatingEitherWay::computeGeneric(const InterfaceState& start) {
|
||||
planning_scene::PlanningScenePtr end;
|
||||
@ -854,12 +862,12 @@ void ConnectingPrivate::compute() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::ostream& ConnectingPrivate::printPendingPairs(std::ostream& os) const {
|
||||
const char* reset = InterfaceState::STATUS_COLOR[3];
|
||||
const char* reset = InterfaceState::colorForStatus(3);
|
||||
for (const auto& candidate : pending) {
|
||||
size_t first = getIndex(*starts(), candidate.first);
|
||||
size_t second = getIndex(*ends(), candidate.second);
|
||||
os << InterfaceState::STATUS_COLOR[candidate.first->priority().status()] << first << reset << ":"
|
||||
<< InterfaceState::STATUS_COLOR[candidate.second->priority().status()] << second << reset << " ";
|
||||
os << InterfaceState::colorForStatus(candidate.first->priority().status()) << first << reset << ":"
|
||||
<< InterfaceState::colorForStatus(candidate.second->priority().status()) << second << reset << " ";
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (pending.empty())
|
||||
os << "---";
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,7 +60,6 @@ static const rclcpp::Logger LOGGER = rclcpp::get_logger("GeneratePlacePose");
|
||||
GeneratePlacePose::GeneratePlacePose(const std::string& name) : GeneratePose(name) {
|
||||
auto& p = properties();
|
||||
p.declare<std::string>("object");
|
||||
p.declare<geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped>("ik_frame");
|
||||
p.declare<bool>("allow_z_flip", false, "allow placing objects upside down");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -69,11 +68,14 @@ void GeneratePlacePose::onNewSolution(const SolutionBase& s) {
|
||||
|
||||
const auto& props = properties();
|
||||
const std::string& object = props.get<std::string>("object");
|
||||
bool frame_found = false;
|
||||
const moveit::core::LinkModel* link = nullptr;
|
||||
scene->getCurrentState().getFrameInfo(object, link, frame_found);
|
||||
std::string msg;
|
||||
if (!scene->getCurrentState().hasAttachedBody(object))
|
||||
msg = "'" + object + "' is not an attached object";
|
||||
if (scene->getCurrentState().getAttachedBody(object)->getShapes().empty())
|
||||
msg = "'" + object + "' has no associated shapes";
|
||||
if (!frame_found)
|
||||
msg = "frame '" + object + "' is not known";
|
||||
if (!link)
|
||||
msg = "frame '" + object + "' is not attached to the robot";
|
||||
if (!msg.empty()) {
|
||||
if (storeFailures()) {
|
||||
InterfaceState state(scene);
|
||||
@ -98,25 +100,20 @@ void GeneratePlacePose::compute() {
|
||||
const moveit::core::RobotState& robot_state = scene->getCurrentState();
|
||||
const auto& props = properties();
|
||||
|
||||
const moveit::core::AttachedBody* object = robot_state.getAttachedBody(props.get<std::string>("object"));
|
||||
// current object_pose w.r.t. planning frame
|
||||
const Eigen::Isometry3d& orig_object_pose = object->getGlobalCollisionBodyTransforms()[0];
|
||||
const std::string& frame_id = props.get<std::string>("object");
|
||||
geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped ik_frame;
|
||||
ik_frame.header.frame_id = frame_id;
|
||||
ik_frame.pose = tf2::toMsg(Eigen::Isometry3d::Identity());
|
||||
|
||||
const moveit::core::AttachedBody* object = robot_state.getAttachedBody(frame_id);
|
||||
const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped& pose_msg = props.get<geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped>("pose");
|
||||
Eigen::Isometry3d target_pose;
|
||||
tf2::fromMsg(pose_msg.pose, target_pose);
|
||||
// target pose w.r.t. planning frame
|
||||
scene->getTransforms().transformPose(pose_msg.header.frame_id, target_pose, target_pose);
|
||||
|
||||
const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped& ik_frame_msg = props.get<geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped>("ik_frame");
|
||||
Eigen::Isometry3d ik_frame;
|
||||
tf2::fromMsg(ik_frame_msg.pose, ik_frame);
|
||||
ik_frame = robot_state.getGlobalLinkTransform(ik_frame_msg.header.frame_id) * ik_frame;
|
||||
Eigen::Isometry3d object_to_ik = orig_object_pose.inverse() * ik_frame;
|
||||
|
||||
// spawn the nominal target object pose, considering flip about z and rotations about z-axis
|
||||
auto spawner = [&s, &scene, &object_to_ik, this](const Eigen::Isometry3d& nominal, uint z_flips,
|
||||
uint z_rotations = 10) {
|
||||
auto spawner = [&s, &scene, &ik_frame, this](const Eigen::Isometry3d& nominal, uint z_flips, uint z_rotations = 10) {
|
||||
for (uint flip = 0; flip <= z_flips; ++flip) {
|
||||
// flip about object's x-axis
|
||||
Eigen::Isometry3d object = nominal * Eigen::AngleAxisd(flip * M_PI, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
|
||||
@ -130,11 +127,12 @@ void GeneratePlacePose::compute() {
|
||||
// target ik_frame's pose w.r.t. planning frame
|
||||
geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped target_pose_msg;
|
||||
target_pose_msg.header.frame_id = scene->getPlanningFrame();
|
||||
target_pose_msg.pose = tf2::toMsg(object * object_to_ik);
|
||||
target_pose_msg.pose = tf2::toMsg(object);
|
||||
|
||||
InterfaceState state(scene);
|
||||
forwardProperties(*s.end(), state); // forward properties from inner solutions
|
||||
state.properties().set("target_pose", target_pose_msg);
|
||||
state.properties().set("ik_frame", ik_frame);
|
||||
|
||||
SubTrajectory trajectory;
|
||||
trajectory.setCost(0.0);
|
||||
@ -146,7 +144,7 @@ void GeneratePlacePose::compute() {
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
uint z_flips = props.get<bool>("allow_z_flip") ? 1 : 0;
|
||||
if (object->getShapes().size() == 1) {
|
||||
if (object && object->getShapes().size() == 1) {
|
||||
switch (object->getShapes()[0]->type) {
|
||||
case shapes::CYLINDER:
|
||||
spawner(target_pose, z_flips);
|
||||
@ -158,7 +156,6 @@ void GeneratePlacePose::compute() {
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case shapes::SPHERE: // keep original orientation and rotate about world's z
|
||||
target_pose.linear() = orig_object_pose.linear();
|
||||
spawner(target_pose, z_flips);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -100,8 +100,8 @@ void ModifyPlanningScene::attachObjects(planning_scene::PlanningScene& scene,
|
||||
bool attach = pair.second.second;
|
||||
if (invert)
|
||||
attach = !attach;
|
||||
obj.object.operation =
|
||||
attach ? (int8_t)moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::ADD : (int8_t)moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::REMOVE;
|
||||
obj.object.operation = attach ? static_cast<int8_t>(moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::ADD) :
|
||||
static_cast<int8_t>(moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::REMOVE);
|
||||
for (const std::string& name : pair.second.first) {
|
||||
obj.object.id = name;
|
||||
scene.processAttachedCollisionObjectMsg(obj);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -248,7 +248,7 @@ bool MoveRelative::compute(const InterfaceState& state, planning_scene::Planning
|
||||
// linear+angular are expressed w.r.t. model frame and thus we need left-multiplication
|
||||
linear = frame_pose.linear() * linear;
|
||||
angular = frame_pose.linear() * angular;
|
||||
auto R = Eigen::AngleAxisd(angular_norm, angular);
|
||||
auto R = Eigen::AngleAxisd(angular_norm, angular); // NOLINT(readability-identifier-naming)
|
||||
auto p = ik_pose_world.translation();
|
||||
target_eigen = Eigen::Translation3d(linear + p - R * p) * (R * ik_pose_world);
|
||||
goto COMPUTE;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,8 +36,11 @@ PickPlaceBase::PickPlaceBase(Stage::pointer&& grasp_stage, const std::string& na
|
||||
return pose;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
const auto& forwarded_props = grasp_stage->forwardedProperties();
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
auto approach = std::make_unique<MoveRelative>(forward ? "approach object" : "retract", cartesian_solver_);
|
||||
approach->setForwardedProperties(forwarded_props);
|
||||
PropertyMap& p = approach->properties();
|
||||
p.property("group").configureInitFrom(Stage::PARENT, "eef_parent_group");
|
||||
p.property("ik_frame").configureInitFrom(Stage::PARENT, init_ik_frame);
|
||||
@ -52,6 +55,7 @@ PickPlaceBase::PickPlaceBase(Stage::pointer&& grasp_stage, const std::string& na
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
auto lift = std::make_unique<MoveRelative>(forward ? "lift object" : "place object", cartesian_solver_);
|
||||
lift->setForwardedProperties(forwarded_props);
|
||||
PropertyMap& p = lift->properties();
|
||||
p.property("group").configureInitFrom(Stage::PARENT, "eef_parent_group");
|
||||
p.property("ik_frame").configureInitFrom(Stage::PARENT, init_ik_frame);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,6 +64,7 @@ SimpleGraspBase::SimpleGraspBase(const std::string& name) : SerialContainer(name
|
||||
void SimpleGraspBase::setup(std::unique_ptr<Stage>&& generator, bool forward) {
|
||||
// properties provided by the grasp generator via its Interface or its PropertyMap
|
||||
const std::set<std::string>& grasp_prop_names = { "object", "eef", "pregrasp", "grasp" };
|
||||
this->setForwardedProperties(grasp_prop_names);
|
||||
|
||||
// insert children at end / front, i.e. normal or reverse order
|
||||
int insertion_position = forward ? -1 : (generator ? 1 : 0);
|
||||
@ -131,8 +132,8 @@ void SimpleGraspBase::setup(std::unique_ptr<Stage>&& generator, bool forward) {
|
||||
attach->setCallback([forward](const planning_scene::PlanningScenePtr& scene, const PropertyMap& p) {
|
||||
const std::string& eef = p.get<std::string>("eef");
|
||||
moveit_msgs::msg::AttachedCollisionObject obj;
|
||||
obj.object.operation = forward ? (int8_t)moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::ADD :
|
||||
(int8_t)moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::REMOVE;
|
||||
obj.object.operation = forward ? static_cast<int8_t>(moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::ADD) :
|
||||
static_cast<int8_t>(moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::REMOVE);
|
||||
obj.link_name = scene->getRobotModel()->getEndEffector(eef)->getEndEffectorParentGroup().second;
|
||||
obj.object.id = p.get<std::string>("object");
|
||||
scene->processAttachedCollisionObjectMsg(obj);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -169,7 +169,7 @@ std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Interface& interface) {
|
||||
os << istate->priority() << " ";
|
||||
return os;
|
||||
}
|
||||
const char* InterfaceState::STATUS_COLOR[] = {
|
||||
const char* InterfaceState::STATUS_COLOR_[] = {
|
||||
"\033[32m", // ENABLED - green
|
||||
"\033[33m", // ARMED - yellow
|
||||
"\033[31m", // PRUNED - red
|
||||
@ -177,8 +177,8 @@ const char* InterfaceState::STATUS_COLOR[] = {
|
||||
};
|
||||
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const InterfaceState::Priority& prio) {
|
||||
// maps InterfaceState::Status values to output (color-changing) prefix
|
||||
os << InterfaceState::STATUS_COLOR[prio.status()] << prio.depth() << ":" << prio.cost()
|
||||
<< InterfaceState::STATUS_COLOR[3];
|
||||
os << InterfaceState::colorForStatus(prio.status()) << prio.depth() << ":" << prio.cost()
|
||||
<< InterfaceState::colorForStatus(3);
|
||||
return os;
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, Interface::Direction dir) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -287,7 +287,7 @@ moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode Task::execute(const SolutionBase& s) {
|
||||
return error_code;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto goal_handle = goal_handle_future.get();
|
||||
const auto& goal_handle = goal_handle_future.get();
|
||||
if (!goal_handle) {
|
||||
RCLCPP_ERROR(node->get_logger(), "Goal was rejected by server");
|
||||
return error_code;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -120,8 +120,8 @@ void spawnObject(PlanningScene& scene, const std::string& name, int type,
|
||||
void attachObject(PlanningScene& scene, const std::string& object, const std::string& link, bool attach) {
|
||||
moveit_msgs::msg::AttachedCollisionObject obj;
|
||||
obj.link_name = link;
|
||||
obj.object.operation =
|
||||
attach ? (int8_t)moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::ADD : (int8_t)moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::REMOVE;
|
||||
obj.object.operation = attach ? static_cast<int8_t>(moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::ADD) :
|
||||
static_cast<int8_t>(moveit_msgs::msg::CollisionObject::REMOVE);
|
||||
obj.object.id = object;
|
||||
scene.processAttachedCollisionObjectMsg(obj);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,9 +17,7 @@ def generate_launch_description():
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Load ExecuteTaskSolutionCapability so we can execute found solutions in simulation
|
||||
move_group_capabilities = {
|
||||
"capabilities": "move_group/ExecuteTaskSolutionCapability"
|
||||
}
|
||||
move_group_capabilities = {"capabilities": "move_group/ExecuteTaskSolutionCapability"}
|
||||
|
||||
# Start the actual move_group node/action server
|
||||
run_move_group_node = Node(
|
||||
|
||||
66
demo/scripts/alternatives.py
Executable file
66
demo/scripts/alternatives.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("mtc_tutorial_alternatives")
|
||||
|
||||
# Use the joint interpolation planner
|
||||
jointPlanner = core.JointInterpolationPlanner()
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a task
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
|
||||
# Start from current robot state
|
||||
currentState = stages.CurrentState("current state")
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the current state to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(currentState)
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfigAlternatives]
|
||||
# The alternatives stage supports multiple execution paths
|
||||
alternatives = core.Alternatives("Alternatives")
|
||||
|
||||
# goal 1
|
||||
goalConfig1 = {
|
||||
"panda_joint1": 1.0,
|
||||
"panda_joint2": -1.0,
|
||||
"panda_joint3": 0.0,
|
||||
"panda_joint4": -2.5,
|
||||
"panda_joint5": 1.0,
|
||||
"panda_joint6": 1.0,
|
||||
"panda_joint7": 1.0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# goal 2
|
||||
goalConfig2 = {
|
||||
"panda_joint1": -3.0,
|
||||
"panda_joint2": -1.0,
|
||||
"panda_joint3": 0.0,
|
||||
"panda_joint4": -2.0,
|
||||
"panda_joint5": 1.0,
|
||||
"panda_joint6": 2.0,
|
||||
"panda_joint7": 0.5,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# First motion plan to compare
|
||||
moveTo1 = stages.MoveTo("Move To Goal Configuration 1", jointPlanner)
|
||||
moveTo1.group = "panda_arm"
|
||||
moveTo1.setGoal(goalConfig1)
|
||||
alternatives.insert(moveTo1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Second motion plan to compare
|
||||
moveTo2 = stages.MoveTo("Move To Goal Configuration 2", jointPlanner)
|
||||
moveTo2.group = "panda_arm"
|
||||
moveTo2.setGoal(goalConfig2)
|
||||
alternatives.insert(moveTo2)
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the alternatives stage to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(alternatives)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigAlternatives]
|
||||
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
time.sleep(1)
|
||||
74
demo/scripts/cartesian.py
Executable file
74
demo/scripts/cartesian.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from std_msgs.msg import Header
|
||||
from geometry_msgs.msg import TwistStamped, Twist, Vector3Stamped, Vector3
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from math import pi
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("mtc_tutorial")
|
||||
|
||||
# [cartesianTut1]
|
||||
group = "panda_arm"
|
||||
# [cartesianTut1]
|
||||
|
||||
# [cartesianTut2]
|
||||
# Cartesian and joint-space interpolation planners
|
||||
cartesian = core.CartesianPath()
|
||||
jointspace = core.JointInterpolationPlanner()
|
||||
# [cartesianTut2]
|
||||
|
||||
# [cartesianTut3]
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
|
||||
# start from current robot state
|
||||
task.add(stages.CurrentState("current state"))
|
||||
# [cartesianTut3]
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfigMoveRelative]
|
||||
# move along x
|
||||
move = stages.MoveRelative("x +0.2", cartesian)
|
||||
move.group = group
|
||||
header = Header(frame_id="world")
|
||||
move.setDirection(Vector3Stamped(header=header, vector=Vector3(0.2, 0, 0)))
|
||||
task.add(move)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigMoveRelative]
|
||||
|
||||
# [cartesianTut4]
|
||||
# move along y
|
||||
move = stages.MoveRelative("y -0.3", cartesian)
|
||||
move.group = group
|
||||
move.setDirection(Vector3Stamped(header=header, vector=Vector3(0, -0.3, 0)))
|
||||
task.add(move)
|
||||
# [cartesianTut4]
|
||||
|
||||
# [cartesianTut5]
|
||||
# rotate about z
|
||||
move = stages.MoveRelative("rz +45°", cartesian)
|
||||
move.group = group
|
||||
move.setDirection(TwistStamped(header=header, twist=Twist(angular=Vector3(0, 0, pi / 4.0))))
|
||||
task.add(move)
|
||||
# [cartesianTut5]
|
||||
|
||||
# [cartesianTut6]
|
||||
# Cartesian motion, defined as joint-space offset
|
||||
move = stages.MoveRelative("joint offset", cartesian)
|
||||
move.group = group
|
||||
move.setDirection(dict(panda_joint1=pi / 6, panda_joint3=-pi / 6))
|
||||
task.add(move)
|
||||
# [cartesianTut6]
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfigMoveTo]
|
||||
# moveTo named posture, using joint-space interplation
|
||||
move = stages.MoveTo("moveTo ready", jointspace)
|
||||
move.group = group
|
||||
move.setGoal("ready")
|
||||
task.add(move)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigMoveTo]
|
||||
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
time.sleep(100)
|
||||
58
demo/scripts/compute_ik.py
Executable file
58
demo/scripts/compute_ik.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped, Pose, Vector3
|
||||
from std_msgs.msg import Header
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("mtc_tutorial_compute_ik")
|
||||
|
||||
# Specify the planning group
|
||||
group = "panda_arm"
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a task
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add a stage to retrieve the current state
|
||||
task.add(stages.CurrentState("current state"))
|
||||
|
||||
# Add a planning stage connecting the generator stages
|
||||
planner = core.PipelinePlanner() # create default planning pipeline
|
||||
task.add(stages.Connect("connect", [(group, planner)])) # operate on group
|
||||
del planner # Delete PipelinePlanner when not explicitly needed anymore
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut12]
|
||||
# Add a Cartesian pose generator
|
||||
generator = stages.GeneratePose("cartesian pose")
|
||||
# [propertyTut12]
|
||||
# Inherit PlanningScene state from "current state" stage
|
||||
generator.setMonitoredStage(task["current state"])
|
||||
# Configure target pose
|
||||
# [propertyTut13]
|
||||
pose = Pose(position=Vector3(z=0.2))
|
||||
generator.pose = PoseStamped(header=Header(frame_id="panda_link8"), pose=pose)
|
||||
# [propertyTut13]
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfigComputeIk]
|
||||
# Wrap Cartesian generator into a ComputeIK stage to yield a joint pose
|
||||
computeIK = stages.ComputeIK("compute IK", generator)
|
||||
computeIK.group = group # Use the group-specific IK solver
|
||||
computeIK.ik_frame = "panda_link8" # Which end-effector frame should reach the target?
|
||||
computeIK.max_ik_solutions = 4 # Limit the number of IK solutions
|
||||
# [propertyTut14]
|
||||
props = computeIK.properties
|
||||
# derive target_pose from child's solution
|
||||
props.configureInitFrom(core.Stage.PropertyInitializerSource.INTERFACE, ["target_pose"])
|
||||
# [propertyTut14]
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the stage to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(computeIK)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigComputeIk]
|
||||
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
|
||||
time.sleep(1) # sleep some time to allow C++ threads to publish their messages
|
||||
21
demo/scripts/current_state.py
Executable file
21
demo/scripts/current_state.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("mtc_tutorial_current_state")
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a task
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the current robot state
|
||||
currentState = stages.CurrentState("current state")
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the stage to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(currentState)
|
||||
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
time.sleep(1)
|
||||
44
demo/scripts/fallbacks.py
Executable file
44
demo/scripts/fallbacks.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("mtc_tutorial_fallbacks")
|
||||
|
||||
# use cartesian and joint interpolation planners
|
||||
cartesianPlanner = core.CartesianPath()
|
||||
jointPlanner = core.JointInterpolationPlanner()
|
||||
|
||||
# initialize the mtc task
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
|
||||
# add the current planning scene state to the task hierarchy
|
||||
currentState = stages.CurrentState("Current State")
|
||||
task.add(currentState)
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfigFallbacks]
|
||||
# create a fallback container to fall back to a different planner
|
||||
# if motion generation fails with the primary one
|
||||
fallbacks = core.Fallbacks("Fallbacks")
|
||||
|
||||
# primary motion plan
|
||||
moveTo1 = stages.MoveTo("Move To Goal Configuration 1", cartesianPlanner)
|
||||
moveTo1.group = "panda_arm"
|
||||
moveTo1.setGoal("extended")
|
||||
fallbacks.insert(moveTo1)
|
||||
|
||||
# fallback motion plan
|
||||
moveTo2 = stages.MoveTo("Move To Goal Configuration 2", jointPlanner)
|
||||
moveTo2.group = "panda_arm"
|
||||
moveTo2.setGoal("extended")
|
||||
fallbacks.insert(moveTo2)
|
||||
|
||||
# add the fallback container to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(fallbacks)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigFallbacks]
|
||||
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
time.sleep(1)
|
||||
29
demo/scripts/fix_collision_objects.py
Executable file
29
demo/scripts/fix_collision_objects.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("mtc_tutorial_current_state")
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a task
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the current state to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(stages.CurrentState("current state"))
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfig]
|
||||
# check for collisions and find corrections
|
||||
fixCollisionObjects = stages.FixCollisionObjects("FixCollisionObjects")
|
||||
|
||||
# cut off length for collision fixing
|
||||
fixCollisionObjects.max_penetration = 0.01
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the stage to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(fixCollisionObjects)
|
||||
# [initAndConfig]
|
||||
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
time.sleep(1)
|
||||
33
demo/scripts/fixed_state.py
Executable file
33
demo/scripts/fixed_state.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.core import planning_scene
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
from moveit.core.planning_scene import PlanningScene
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("mtc_tutorial_current_state")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a task
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfigFixedState]
|
||||
# Initialize a PlanningScene for use in a FixedState stage
|
||||
task.loadRobotModel() # load the robot model (usually done in init())
|
||||
planningScene = PlanningScene(task.getRobotModel())
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a FixedState stage and pass the created PlanningScene as its state
|
||||
fixedState = stages.FixedState("fixed state")
|
||||
fixedState.setState(planningScene)
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the stage to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(fixedState)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigFixedState]
|
||||
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
|
||||
del planningScene # Avoid ClassLoader warning by destroying the RobotModel
|
||||
time.sleep(1)
|
||||
51
demo/scripts/generate_pose.py
Executable file
51
demo/scripts/generate_pose.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("mtc_tutorial_compute_ik")
|
||||
|
||||
# Specify the planning group
|
||||
group = "panda_arm"
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a task
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the current robot state
|
||||
currentState = stages.CurrentState("current state")
|
||||
task.add(currentState)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a planner instance that is used to connect
|
||||
# the current state to the grasp approach pose
|
||||
pipelinePlanner = core.PipelinePlanner()
|
||||
pipelinePlanner.planner = "RRTConnectkConfigDefault"
|
||||
planners = [(group, pipelinePlanner)]
|
||||
|
||||
# Connect the two stages
|
||||
connect = stages.Connect("connect1", planners)
|
||||
connect.properties.configureInitFrom(core.Stage.PropertyInitializerSource.PARENT)
|
||||
task.add(connect)
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfigGeneratePose]
|
||||
# create an example pose wrt. the origin of the
|
||||
# panda arm link8
|
||||
pose = PoseStamped()
|
||||
pose.header.frame_id = "panda_link8"
|
||||
|
||||
# Calculate the inverse kinematics for the current robot state
|
||||
generatePose = stages.GeneratePose("generate pose")
|
||||
|
||||
# spwan a pose whenever there is a solution of the monitored stage
|
||||
generatePose.setMonitoredStage(task["current state"])
|
||||
generatePose.pose = pose
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the stage to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(generatePose)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigGeneratePose]
|
||||
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
time.sleep(1)
|
||||
42
demo/scripts/merger.py
Executable file
42
demo/scripts/merger.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("mtc_tutorial_merger")
|
||||
|
||||
# use the joint interpolation planner
|
||||
planner = core.JointInterpolationPlanner()
|
||||
|
||||
# the task will contain our stages
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
|
||||
# start from current robot state
|
||||
currentState = stages.CurrentState("current state")
|
||||
task.add(currentState)
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfigMerger]
|
||||
# the merger plans for two parallel execution paths
|
||||
merger = core.Merger("Merger")
|
||||
|
||||
# first simultaneous execution
|
||||
moveTo1 = stages.MoveTo("Move To Home", planner)
|
||||
moveTo1.group = "hand"
|
||||
moveTo1.setGoal("close")
|
||||
merger.insert(moveTo1)
|
||||
|
||||
# second simultaneous execution
|
||||
moveTo2 = stages.MoveTo("Move To Ready", planner)
|
||||
moveTo2.group = "panda_arm"
|
||||
moveTo2.setGoal("extended")
|
||||
merger.insert(moveTo2)
|
||||
|
||||
# add the merger stage to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(merger)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigMerger]
|
||||
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
time.sleep(1)
|
||||
49
demo/scripts/modify_planning_scene.py
Executable file
49
demo/scripts/modify_planning_scene.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from moveit_msgs.msg import CollisionObject
|
||||
from shape_msgs.msg import SolidPrimitive
|
||||
from geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("mtc_tutorial_modify_planning_scene")
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a task
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the current state to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(stages.CurrentState("current state"))
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfigModifyPlanningScene]
|
||||
# Specify object parameters
|
||||
object_name = "grasp_object"
|
||||
object_radius = 0.02
|
||||
|
||||
objectPose = PoseStamped()
|
||||
objectPose.header.frame_id = "world"
|
||||
objectPose.pose.orientation.x = 1.0
|
||||
objectPose.pose.position.x = 0.30702
|
||||
objectPose.pose.position.y = 0.0
|
||||
objectPose.pose.position.z = 0.285
|
||||
|
||||
object = CollisionObject()
|
||||
object.header.frame_id = "world"
|
||||
object.id = object_name
|
||||
sphere = SolidPrimitive()
|
||||
sphere.type = sphere.SPHERE
|
||||
sphere.dimensions.insert(sphere.SPHERE_RADIUS, object_radius)
|
||||
|
||||
object.primitives.append(sphere)
|
||||
object.primitive_poses.append(objectPose.pose)
|
||||
object.operation = object.ADD
|
||||
|
||||
modifyPlanningScene = stages.ModifyPlanningScene("modify planning scene")
|
||||
modifyPlanningScene.addObject(object)
|
||||
task.add(modifyPlanningScene)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigModifyPlanningScene]
|
||||
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
time.sleep(1)
|
||||
173
demo/scripts/pickplace.py
Executable file
173
demo/scripts/pickplace.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,173 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from moveit_commander import PlanningSceneInterface
|
||||
from geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped, TwistStamped
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("pickplace")
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut1]
|
||||
# Specify robot parameters
|
||||
arm = "panda_arm"
|
||||
eef = "hand"
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut1]
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut2]
|
||||
# Specify object parameters
|
||||
object_name = "grasp_object"
|
||||
object_radius = 0.02
|
||||
|
||||
# Start with a clear planning scene
|
||||
psi = PlanningSceneInterface(synchronous=True)
|
||||
psi.remove_world_object()
|
||||
|
||||
# [initCollisionObject]
|
||||
# Grasp object properties
|
||||
objectPose = PoseStamped()
|
||||
objectPose.header.frame_id = "world"
|
||||
objectPose.pose.orientation.x = 1.0
|
||||
objectPose.pose.position.x = 0.30702
|
||||
objectPose.pose.position.y = 0.0
|
||||
objectPose.pose.position.z = 0.285
|
||||
# [initCollisionObject]
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the grasp object to the planning scene
|
||||
psi.add_box(object_name, objectPose, size=[0.1, 0.05, 0.03])
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut2]
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut3]
|
||||
# Create a task
|
||||
task = core.Task("PandaPickPipelineExample")
|
||||
task.enableIntrospection()
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut3]
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut4]
|
||||
# Start with the current state
|
||||
task.add(stages.CurrentState("current"))
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfigConnect]
|
||||
# Create a planner instance that is used to connect
|
||||
# the current state to the grasp approach pose
|
||||
pipeline = core.PipelinePlanner()
|
||||
pipeline.planner = "RRTConnectkConfigDefault"
|
||||
planners = [(arm, pipeline)]
|
||||
|
||||
# Connect the two stages
|
||||
task.add(stages.Connect("connect1", planners))
|
||||
# [initAndConfigConnect]
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut4]
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut5]
|
||||
# [initAndConfigGenerateGraspPose]
|
||||
# The grasp generator spawns a set of possible grasp poses around the object
|
||||
grasp_generator = stages.GenerateGraspPose("Generate Grasp Pose")
|
||||
grasp_generator.angle_delta = 0.2
|
||||
grasp_generator.pregrasp = "open"
|
||||
grasp_generator.grasp = "close"
|
||||
grasp_generator.setMonitoredStage(task["current"]) # Generate solutions for all initial states
|
||||
# [initAndConfigGenerateGraspPose]
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut5]
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut6]
|
||||
# [initAndConfigSimpleGrasp]
|
||||
# SimpleGrasp container encapsulates IK calculation of arm pose as well as finger closing
|
||||
simpleGrasp = stages.SimpleGrasp(grasp_generator, "Grasp")
|
||||
# Set frame for IK calculation in the center between the fingers
|
||||
ik_frame = PoseStamped()
|
||||
ik_frame.header.frame_id = "panda_hand"
|
||||
ik_frame.pose.position.z = 0.1034
|
||||
simpleGrasp.setIKFrame(ik_frame)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigSimpleGrasp]
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut6]
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut7]
|
||||
# [initAndConfigPick]
|
||||
# Pick container comprises approaching, grasping (using SimpleGrasp stage), and lifting of object
|
||||
pick = stages.Pick(simpleGrasp, "Pick")
|
||||
pick.eef = eef
|
||||
pick.object = object_name
|
||||
|
||||
# Twist to approach the object
|
||||
approach = TwistStamped()
|
||||
approach.header.frame_id = "world"
|
||||
approach.twist.linear.z = -1.0
|
||||
pick.setApproachMotion(approach, 0.03, 0.1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Twist to lift the object
|
||||
lift = TwistStamped()
|
||||
lift.header.frame_id = "panda_hand"
|
||||
lift.twist.linear.z = -1.0
|
||||
pick.setLiftMotion(lift, 0.03, 0.1)
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut7]
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut8]
|
||||
# Add the pick stage to the task's stage hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(pick)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigPick]
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut8]
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut9]
|
||||
# Connect the Pick stage with the following Place stage
|
||||
task.add(stages.Connect("connect2", planners))
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut9]
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut10]
|
||||
# [initAndConfigGeneratePlacePose]
|
||||
# Define the pose that the object should have after placing
|
||||
placePose = objectPose
|
||||
placePose.pose.position.y += 0.2 # shift object by 20cm along y axis
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate Cartesian place poses for the object
|
||||
place_generator = stages.GeneratePlacePose("Generate Place Pose")
|
||||
place_generator.setMonitoredStage(task["Pick"])
|
||||
place_generator.object = object_name
|
||||
place_generator.pose = placePose
|
||||
# [initAndConfigGeneratePlacePose]
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut10]
|
||||
|
||||
# [initAndConfigSimpleUnGrasp]
|
||||
# The SimpleUnGrasp container encapsulates releasing the object at the given Cartesian pose
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut11]
|
||||
simpleUnGrasp = stages.SimpleUnGrasp(place_generator, "UnGrasp")
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut11]
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut12]
|
||||
# [initAndConfigPlace]
|
||||
# Place container comprises placing, ungrasping, and retracting
|
||||
place = stages.Place(simpleUnGrasp, "Place")
|
||||
place.eef = eef
|
||||
place.object = object_name
|
||||
place.eef_frame = "panda_link8"
|
||||
# [initAndConfigSimpleUnGrasp]
|
||||
|
||||
# Twist to retract from the object
|
||||
retract = TwistStamped()
|
||||
retract.header.frame_id = "world"
|
||||
retract.twist.linear.z = 1.0
|
||||
place.setRetractMotion(retract, 0.03, 0.1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Twist to place the object
|
||||
placeMotion = TwistStamped()
|
||||
placeMotion.header.frame_id = "panda_hand"
|
||||
placeMotion.twist.linear.z = 1.0
|
||||
place.setPlaceMotion(placeMotion, 0.03, 0.1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the place pipeline to the task's hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(place)
|
||||
# [initAndConfigPlace]
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut12]
|
||||
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut13]
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
|
||||
# avoid ClassLoader warning
|
||||
del pipeline
|
||||
del planners
|
||||
# [pickAndPlaceTut13]
|
||||
|
||||
# Prevent the program from exiting, giving you the opportunity to inspect solutions in rviz
|
||||
time.sleep(3600)
|
||||
100
demo/scripts/properties.py
Normal file
100
demo/scripts/properties.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.task_constructor import core, stages
|
||||
from geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
from moveit.python_tools import roscpp_init
|
||||
|
||||
roscpp_init("mtc_tutorial")
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a task container
|
||||
task = core.Task()
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut10]
|
||||
# Create a current state to capture the current planning scene state
|
||||
currentState = stages.CurrentState("Current State")
|
||||
# [propertyTut10]
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut1]
|
||||
# Create a property
|
||||
p = core.Property()
|
||||
|
||||
# Set a descriptive string to describe the properties function
|
||||
p.setDescription("Foo Property")
|
||||
# [propertyTut1]
|
||||
|
||||
# Set the current and the default value
|
||||
p.setValue("Bar")
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut2]
|
||||
# Check if the property is defined
|
||||
assert p.defined()
|
||||
# [propertyTut2]
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut3]
|
||||
# Retrieve the stored value
|
||||
print(p.value())
|
||||
|
||||
# Retrieve the default value
|
||||
print(p.defaultValue())
|
||||
|
||||
# Retrieve the description
|
||||
print(p.description())
|
||||
# [propertyTut3]
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut4]
|
||||
# Create a property map
|
||||
pm = core.PropertyMap()
|
||||
props = {"prop1": "test", "prop2": 21, "prop3": PoseStamped(), "prop4": 5.4}
|
||||
pm.update(props)
|
||||
# [propertyTut4]
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut5]
|
||||
# Add a property to the property map using the pythonic way
|
||||
pm["prop5"] = 2
|
||||
# [propertyTut5]
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut6]
|
||||
# Return the value of a property
|
||||
print(pm["prop5"])
|
||||
# [propertyTut6]
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut7]
|
||||
# Return the underlying property object
|
||||
p2 = pm.property("prop5")
|
||||
# [propertyTut7]
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut8]
|
||||
# Iterate through all the values in the property map
|
||||
print("\n")
|
||||
for i in pm:
|
||||
print(i, "\t\t", pm[i])
|
||||
print("\n")
|
||||
# [propertyTut8]
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut9]
|
||||
# A new property map can also be configured using an existing one
|
||||
# You can also only use a subset of the properties that should be configured.
|
||||
pm2 = core.PropertyMap()
|
||||
pm.exposeTo(pm2, ["prop2", "prop4"])
|
||||
# [propertyTut9]
|
||||
|
||||
# Lets test that by printing out our properties
|
||||
for i in pm2:
|
||||
print(i, "\t\t", pm2[i])
|
||||
print("\n")
|
||||
|
||||
# [propertyTut11]
|
||||
# Access the property map of the stage
|
||||
props = currentState.properties
|
||||
# [propertyTut11]
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the stage to the task hierarchy
|
||||
task.add(currentState)
|
||||
|
||||
if task.plan():
|
||||
task.publish(task.solutions[0])
|
||||
|
||||
time.sleep(100)
|
||||
@ -3,9 +3,8 @@
|
||||
#############
|
||||
|
||||
## Add gtest based cpp test target and link libraries
|
||||
if (CATKIN_ENABLE_TESTING)
|
||||
find_package(rostest REQUIRED)
|
||||
|
||||
add_rostest_gtest(pick_place_test pick_place.test pick_place_test.cpp)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(pick_place_test ${PROJECT_NAME}_pick_place_task ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
|
||||
if (BUILD_TESTING)
|
||||
find_package(ament_cmake_gtest REQUIRED)
|
||||
ament_add_gtest(pick_place_test pick_place_test.cpp)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(pick_place_test ${PROJECT_NAME}_pick_place_task)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Migration Guide from ROS1
|
||||
|
||||
* Default C++ standard set to 17
|
||||
* CMake version set to 3.5
|
||||
* PipelinePlanner's constructor now have a node `rclcpp::Node::SharedPtr` as an argument to load the `PlanningPipeline`'s parameters
|
||||
* `Task::loadRobotModel` have a node as a parameter and the user have to call loadRobotModel explicitly otherwise init will throw an exception
|
||||
@ -99,7 +99,7 @@ QModelIndex LocalTaskModel::index(int row, int column, const QModelIndex& parent
|
||||
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(dynamic_cast<ContainerBase*>(node(parent)));
|
||||
ContainerBase* p = static_cast<ContainerBase*>(node(parent));
|
||||
if (!p || row < 0 || (size_t)row >= p->numChildren())
|
||||
if (!p || row < 0 || static_cast<size_t>(row) >= p->numChildren())
|
||||
return QModelIndex();
|
||||
|
||||
Node* child = nullptr;
|
||||
@ -149,7 +149,7 @@ QVariant LocalTaskModel::data(const QModelIndex& index, int role) const {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
return QString::fromStdString(n->name());
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
return (uint)n->solutions().size();
|
||||
return static_cast<uint>(n->solutions().size());
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -180,7 +180,7 @@ bool LocalTaskModel::removeRows(int row, int count, const QModelIndex& parent) {
|
||||
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(dynamic_cast<ContainerBase*>(node(parent)));
|
||||
ContainerBase* c = static_cast<ContainerBase*>(node(parent));
|
||||
if (row < 0 || (size_t)row + count > c->numChildren())
|
||||
if (row < 0 || static_cast<size_t>(row + count) > c->numChildren())
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
|
||||
beginRemoveRows(parent, row, row + count - 1);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -159,7 +159,7 @@ RemoteTaskModel::Node* RemoteTaskModel::node(const QModelIndex& index) const {
|
||||
|
||||
// internal pointer refers to parent node
|
||||
Node* parent = static_cast<Node*>(index.internalPointer());
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(index.row() >= 0 && (size_t)index.row() < parent->children_.size());
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(index.row() >= 0 && static_cast<size_t>(index.row()) < parent->children_.size());
|
||||
return parent->children_.at(index.row()).get();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -218,7 +218,7 @@ QModelIndex RemoteTaskModel::index(int row, int column, const QModelIndex& paren
|
||||
return QModelIndex();
|
||||
|
||||
Node* p = node(parent);
|
||||
if (!p || row < 0 || (size_t)row >= p->children_.size())
|
||||
if (!p || row < 0 || static_cast<size_t>(row) >= p->children_.size())
|
||||
return QModelIndex();
|
||||
|
||||
p->children_[row]->node_flags_ |= WAS_VISITED;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -198,7 +198,7 @@ void TaskDisplay::changedRobotDescription() {
|
||||
loadRobotModel();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void TaskDisplay::taskDescriptionCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::TaskDescription::ConstSharedPtr msg) {
|
||||
void TaskDisplay::taskDescriptionCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::TaskDescription::ConstSharedPtr& msg) {
|
||||
setStatus(rviz_common::properties::StatusProperty::Ok, "Task Monitor", "OK");
|
||||
requestPanel();
|
||||
task_list_model_->processTaskDescriptionMessage(*msg, base_ns_ + GET_SOLUTION_SERVICE "_" + msg->task_id);
|
||||
@ -222,12 +222,12 @@ void TaskDisplay::taskDescriptionCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::Tas
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void TaskDisplay::taskStatisticsCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::TaskStatistics::ConstSharedPtr msg) {
|
||||
void TaskDisplay::taskStatisticsCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::TaskStatistics::ConstSharedPtr& msg) {
|
||||
setStatus(rviz_common::properties::StatusProperty::Ok, "Task Monitor", "OK");
|
||||
task_list_model_->processTaskStatisticsMessage(*msg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void TaskDisplay::taskSolutionCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::Solution::ConstSharedPtr msg) {
|
||||
void TaskDisplay::taskSolutionCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::Solution::ConstSharedPtr& msg) {
|
||||
setStatus(rviz_common::properties::StatusProperty::Ok, "Task Monitor", "OK");
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const DisplaySolutionPtr& s = task_list_model_->processSolutionMessage(*msg);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -116,9 +116,9 @@ private Q_SLOTS:
|
||||
void onTasksRemoved(const QModelIndex& parent, int first, int last);
|
||||
void onTaskDataChanged(const QModelIndex& topLeft, const QModelIndex& bottomRight);
|
||||
|
||||
void taskDescriptionCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::TaskDescription::ConstSharedPtr msg);
|
||||
void taskStatisticsCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::TaskStatistics::ConstSharedPtr msg);
|
||||
void taskSolutionCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::Solution::ConstSharedPtr msg);
|
||||
void taskDescriptionCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::TaskDescription::ConstSharedPtr& msg);
|
||||
void taskStatisticsCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::TaskStatistics::ConstSharedPtr& msg);
|
||||
void taskSolutionCB(const moveit_task_constructor_msgs::msg::Solution::ConstSharedPtr& msg);
|
||||
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
/** @brief A Node which is registered with the main executor (used in the "update" thread).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -240,7 +240,7 @@ TaskViewPrivate::TaskViewPrivate(TaskView* view) : q_ptr(view) {
|
||||
meta_model->setMimeTypes({ factory->mimeType() });
|
||||
tasks_view->setModel(meta_model);
|
||||
QObject::connect(meta_model, SIGNAL(rowsInserted(QModelIndex, int, int)), q_ptr,
|
||||
SLOT(_q_configureInsertedModels(QModelIndex, int, int)));
|
||||
SLOT(configureInsertedModels(QModelIndex, int, int)));
|
||||
|
||||
tasks_view->setSelectionMode(QAbstractItemView::ExtendedSelection);
|
||||
tasks_view->setAcceptDrops(true);
|
||||
@ -276,7 +276,7 @@ void TaskViewPrivate::configureExistingModels() {
|
||||
configureTaskListModel(meta_model->getTaskListModel(meta_model->index(row, 0)).first);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void TaskViewPrivate::_q_configureInsertedModels(const QModelIndex& parent, int first, int last) {
|
||||
void TaskViewPrivate::configureInsertedModels(const QModelIndex& parent, int first, int last) {
|
||||
if (parent.isValid() && !parent.parent().isValid()) { // top-level task items inserted
|
||||
int expand = q_ptr->initial_task_expand->getOptionInt();
|
||||
for (int row = first; row <= last; ++row) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -158,7 +158,7 @@ protected Q_SLOTS:
|
||||
void onOldTaskHandlingChanged();
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
Q_PRIVATE_SLOT(d_ptr, void _q_configureInsertedModels(QModelIndex, int, int));
|
||||
Q_PRIVATE_SLOT(d_ptr, void configureInsertedModels(QModelIndex, int, int));
|
||||
|
||||
Q_SIGNALS:
|
||||
void oldTaskHandlingChanged(int old_task_handling);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -82,9 +82,8 @@ public:
|
||||
void configureTaskListModel(TaskListModel* model);
|
||||
/// configure all TaskListModels that were already created when TaskView gets instantiated
|
||||
void configureExistingModels();
|
||||
// NOLINTNEXTLINE(readability-identifier-naming)
|
||||
/// configure newly inserted models
|
||||
void _q_configureInsertedModels(const QModelIndex& parent, int first, int last);
|
||||
void configureInsertedModels(const QModelIndex& parent, int first, int last);
|
||||
|
||||
/// unlock locked_display_ if given display is different
|
||||
void lock(TaskDisplay* display);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -236,8 +236,8 @@ int main(int argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
// NOLINTNEXTLINE(clang-analyzer-cplusplus.NewDeleteLeaks)
|
||||
QTimer::singleShot(0, [&]() {
|
||||
::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv);
|
||||
auto testResult = RUN_ALL_TESTS();
|
||||
app.exit(testResult);
|
||||
auto test_result = RUN_ALL_TESTS();
|
||||
app.exit(test_result);
|
||||
});
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -415,11 +415,11 @@ bool FlatMergeProxyModel::insertModel(QAbstractItemModel* model, int pos) {
|
||||
return false; // all models must have same column count
|
||||
|
||||
// limit pos to range [0, modelCount()]
|
||||
if (pos > 0 && pos > (int)modelCount())
|
||||
if (pos > 0 && pos > static_cast<int>(modelCount()))
|
||||
pos = modelCount();
|
||||
if (pos < 0)
|
||||
pos = modelCount() + std::max<int>(pos + 1, -modelCount());
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(pos >= 0 && pos <= (int)modelCount());
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(pos >= 0 && pos <= static_cast<int>(modelCount()));
|
||||
auto it = d_ptr->data_.begin();
|
||||
std::advance(it, pos);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -481,9 +481,9 @@ bool FlatMergeProxyModel::removeModel(int pos) {
|
||||
pos = modelCount() + pos + 1;
|
||||
if (pos < 0)
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
if (pos >= (int)modelCount())
|
||||
if (pos >= static_cast<int>(modelCount()))
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(pos >= 0 && pos < (int)modelCount());
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(pos >= 0 && pos < static_cast<int>(modelCount()));
|
||||
|
||||
auto it = d_ptr->data_.begin();
|
||||
std::advance(it, pos);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -269,7 +269,7 @@ QModelIndex TreeMergeProxyModel::index(int row, int column, const QModelIndex& p
|
||||
return QModelIndex();
|
||||
|
||||
if (!parent.isValid()) { // top-level / group items
|
||||
if ((size_t)row >= d_ptr->data_.size())
|
||||
if (static_cast<size_t>(row) >= d_ptr->data_.size())
|
||||
return QModelIndex();
|
||||
|
||||
// for group items, internal pointer refers to this model
|
||||
@ -397,11 +397,11 @@ bool TreeMergeProxyModel::insertModel(const QString& name, QAbstractItemModel* m
|
||||
return false; // model can only inserted once
|
||||
|
||||
// limit pos to range [0, modelCount()]
|
||||
if (pos > 0 && pos > (int)modelCount())
|
||||
if (pos > 0 && pos > static_cast<int>(modelCount()))
|
||||
pos = modelCount();
|
||||
if (pos < 0)
|
||||
pos = modelCount() + std::max<int>(pos + 1, -modelCount());
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(pos >= 0 && pos <= (int)modelCount());
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(pos >= 0 && pos <= static_cast<int>(modelCount()));
|
||||
auto it = d_ptr->data_.begin();
|
||||
std::advance(it, pos);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -460,9 +460,9 @@ bool TreeMergeProxyModel::removeModel(int pos) {
|
||||
pos = modelCount() + pos + 1;
|
||||
if (pos < 0)
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
if (pos >= (int)modelCount())
|
||||
if (pos >= static_cast<int>(modelCount()))
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(pos >= 0 && pos < (int)modelCount());
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(pos >= 0 && pos < static_cast<int>(modelCount()));
|
||||
auto it = d_ptr->data_.begin();
|
||||
std::advance(it, pos);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ bool MarkerVisualization::createMarkers(rviz_common::DisplayContext* context, Og
|
||||
// fetch transform from planning_frame_ to rviz' fixed frame
|
||||
const std::string& fixed_frame = context->getFrameManager()->getFixedFrame();
|
||||
Ogre::Quaternion quat;
|
||||
Ogre::Vector3 pos;
|
||||
Ogre::Vector3 pos = Ogre::Vector3::ZERO;
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
auto tf_wrapper = std::dynamic_pointer_cast<rviz_default_plugins::transformation::TFWrapper>(
|
||||
@ -157,7 +157,7 @@ void MarkerVisualization::update(MarkerData& data, const planning_scene::Plannin
|
||||
auto frame_it = ns_it->second.frames_.find(marker.header.frame_id);
|
||||
Q_ASSERT(frame_it != ns_it->second.frames_.end()); // we have created all of them
|
||||
|
||||
const Eigen::Quaterniond q = (Eigen::Quaterniond)pose.linear();
|
||||
const Eigen::Quaterniond q{ pose.linear() };
|
||||
const Eigen::Vector3d& p = pose.translation();
|
||||
frame_it->second->setOrientation(Ogre::Quaternion(q.w(), q.x(), q.y(), q.z()));
|
||||
frame_it->second->setPosition(Ogre::Vector3(p.x(), p.y(), p.z()));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -257,7 +257,7 @@ void TaskSolutionVisualization::clearTrail() {
|
||||
void TaskSolutionVisualization::changedLoopDisplay() {
|
||||
// restart animation if current_state_ is at end and looping got activated
|
||||
if (displaying_solution_ && loop_display_property_->getBool() && slider_panel_ && slider_panel_->isVisible() &&
|
||||
current_state_ + 1 >= (int)displaying_solution_->getWayPointCount()) {
|
||||
current_state_ + 1 >= static_cast<int>(displaying_solution_->getWayPointCount())) {
|
||||
current_state_ = -1;
|
||||
slider_panel_->pauseButton(false);
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -482,7 +482,7 @@ void TaskSolutionVisualization::renderWayPoint(size_t index, int previous_index)
|
||||
auto idx_pair = displaying_solution_->indexPair(index);
|
||||
scene = displaying_solution_->scene(idx_pair);
|
||||
|
||||
if (previous_index < 0 || previous_index >= (int)waypoint_count ||
|
||||
if (previous_index < 0 || previous_index >= static_cast<int>(waypoint_count) ||
|
||||
displaying_solution_->indexPair(previous_index).first != idx_pair.first) {
|
||||
// switch to new stage: show new planning scene
|
||||
renderPlanningScene(scene);
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user